Content mapping for WooCommerce: Aligning your catalog with the buyer journey
Content mapping for WooCommerce is the strategic alignment of your blog articles and guides with the specific stages of a shopper’s path to purchase. Successful ecommerce SEO isn’t just about capturing traffic; it’s about building a high-converting bridge between a user’s search query and your product catalog. I have found that most merchants treat their blog and their catalog as two separate islands, which results in a bloated site that fails to drive revenue.
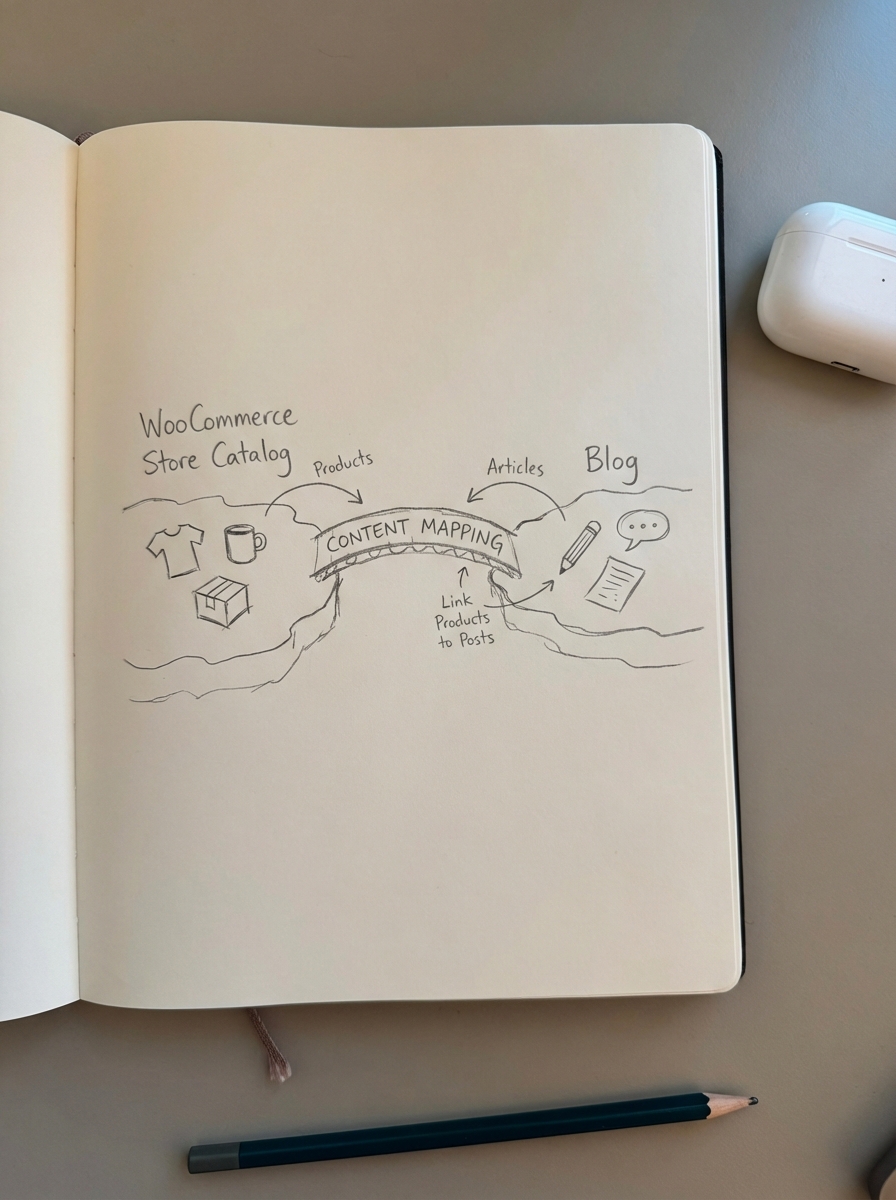
When you map content effectively, you transform your blog from a generic content repository into a high-traffic entry point that feeds directly into your category pages. These categories are where the actual SEO heavy lifting happens. By understanding customer motivations and mapping them to McKinsey & Company’s Customer Decision Journey – spanning initial consideration, active evaluation, closure, and post-purchase – you can ensure your content inventory actually serves your bottom line.
The catalog-driven content mapping framework
An effective ecommerce content map goes beyond simple keyword volume; it prioritizes search intent. I’ve seen that the most successful stores move users from vague problems to specific SKUs by categorizing content into three distinct funnel stages. This ensures you aren’t just producing “thought leadership” content that fails to rank, but rather purposeful assets that assist the sale.
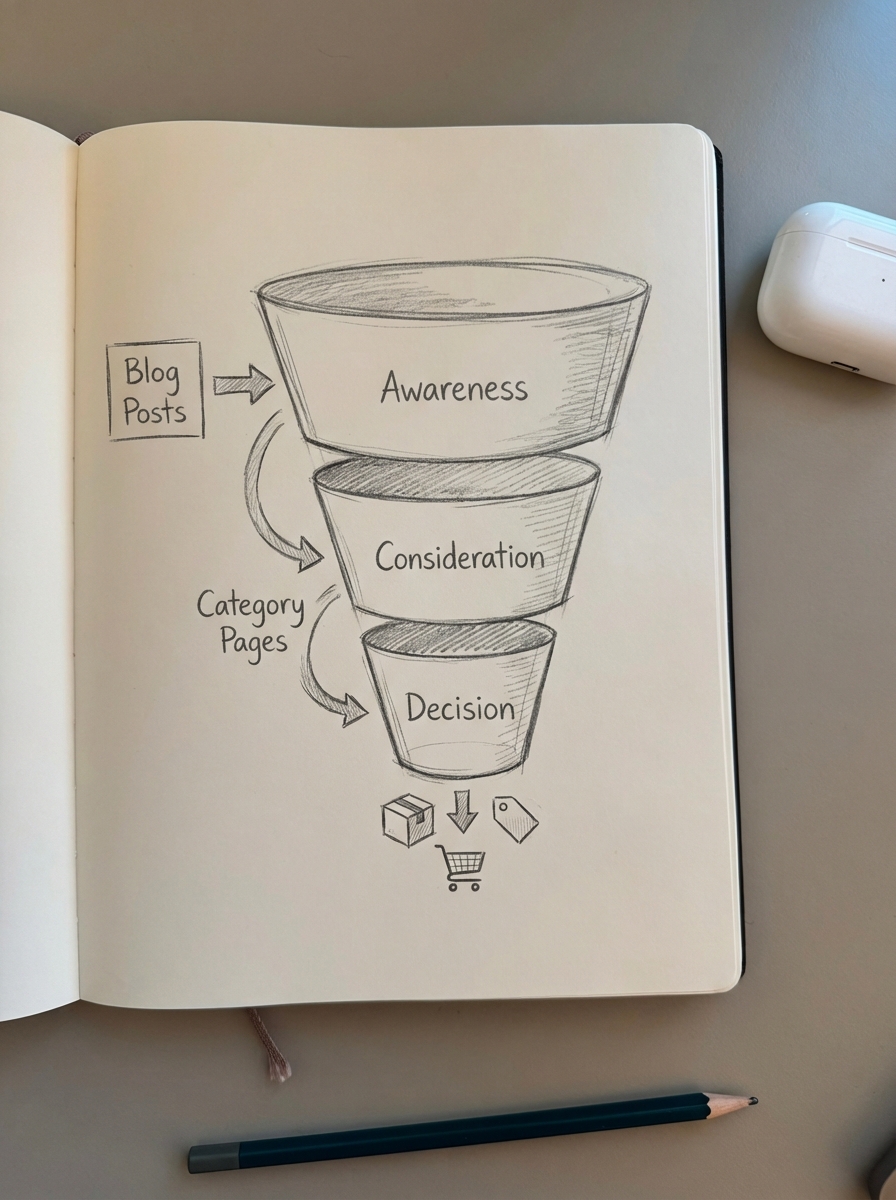
Awareness (Top of Funnel)
At this stage, the user has a problem but might not realize your product is the solution. They are searching for educational guides or troubleshooting tips to address a pain point. We focus on capturing broad search volume and establishing topical authority here.
- Educational “how-to” guides and troubleshooting articles.
- Informational listicles that address high-level problems.
- “What is” content that explains industry concepts.
- Example: A merchant selling specialty coffee equipment maps the query “why does my espresso taste sour” to a guide on extraction variables.
Consideration (Middle of Funnel)
The user has identified the solution – they need a specific type of product – but they are now in the active evaluation phase. They are comparing alternatives and looking for expert validation to narrow down their choices. This is the moment to move users from the blog into your strategic topic clusters to show off your expertise.
- Comparative buying guides and “Best of” lists.
- Expert webinars or in-depth technical breakdowns.
- Case studies and expert comparative analyses.
- Example: “Manual vs. Automatic Espresso Machines: Which is right for you?”
Decision (Bottom of Funnel)
The user is ready to close the deal. They are searching for specific brands, models, or highly transactional terms that indicate they are in the closure phase. At this point, the goal is to convert the visit into a sale on a product or category page through high-intent descriptors.
- Product reviews and setup guides.
- Optimized category descriptions that highlight specific benefits.
- Concrete evidence of value and real-world success stories.
- Example: “Breville Bambino Plus Review and Setup Guide.”
Workflow for mapping WooCommerce content
Mapping your catalog manually is a meticulous process, but it is necessary for building a coherent content production workflow. I recommend focusing on your category pages first. In my experience, most ecommerce sites benefit more from optimizing your category names to be more specific than they do from writing a dozen new blog posts.
- First, extract and segment your catalog data by looking at your WooCommerce category structure. Each main category should be treated as a “Pillar.” Identify the “jobs to be done” for each category – for instance, if you sell hiking boots, the job is providing dry feet and ankle support.
- Next, identify search intent gaps by reviewing Google Search Console data and site search logs. If you have high impressions for a query but no page that answers it, you have found a content gap. Use a SERP-based clustering tool to group these queries so you don’t create duplicate content.
- Then, map your keyword clusters to your URL structure. Transactional clusters belong on category or product pages, while informational clusters belong on the blog. Commercial investigation keywords often perform best as long-form guides that link back to your categories.
- Finally, build the internal link bridge. This is the most critical step. Your informational blog posts must link to your categories using descriptive anchor text. I have seen stores achieve a massive lift in rankings just by adding three to five contextual internal links from a high-traffic post to a struggling category page.
Scaling your content map with automation
The primary challenge with manual content mapping is that WooCommerce catalogs are dynamic. Products go out of stock, prices fluctuate, and new categories are added constantly. A static map in a spreadsheet becomes obsolete almost immediately, which is why we advocate for scaling content production with automation.
We built ContentGecko to be “catalog-aware” to solve this exact problem. By using a WordPress connector plugin, your content strategy stays synced with your live database. This allows for automated SEO intelligence that identifies which categories lack topical support and automatically drafts the necessary guides.
Beyond initial creation, SEO content automation ensures your content is never “dead-end.” If a product in a “Best of” list goes out of stock, an automated system can update the mention or swap it for an available SKU. This level of catalog-synced maintenance prevents the broken user experiences that kill conversion rates on traditional, static blogs.
Common pitfalls in ecommerce content mapping
I often see marketers prioritize high-volume “thought leadership” topics because they look impressive in monthly traffic reports. However, if that traffic doesn’t map back to a product or category in your WooCommerce store, it is wasted effort. You should prioritize high-intent, product-aligned keywords over high-volume irrelevant terms every time.
- Ignoring the category page: Your content map should always lead the user back to a category, as these are your most powerful SEO assets.
- Over-clustering: Avoid creating a new page for every slight keyword variation. Use specialized keyword clustering tools to see if Google treats two terms as having the same intent.
- Static content: Search intent and SERP features change over time. You must periodically audit your map and iterate your content like a product – launching an MVP and refining it based on real-world performance data.
- Inaccurate data: Do not rely solely on third-party keyword databases, as their search volume and competition data are often off by a significant margin.
TL;DR
Content mapping for WooCommerce requires aligning your product catalog with the Awareness, Consideration, and Decision stages of the buyer journey. To succeed, you must prioritize your category pages as the ultimate traffic destination, use keyword clustering to organize your strategy, and leverage automation to keep content synced with your live inventory. By focusing on solving user problems rather than just chasing volume, you create an SEO strategy that actually converts visitors into customers.
