What is SEO writing
SEO writing is the strategic process of planning and creating content designed to satisfy both search engine algorithms and human intent to drive profitable organic traffic. In an ecommerce environment, this means moving beyond static product descriptions to build a content ecosystem – comprising blog posts, topic clusters, and enhanced category guides – that answers buyer questions and funnels users toward a conversion.
Start with search intent rather than volume
I have seen many marketing teams waste thousands of dollars on “thought leadership” pieces that never rank because they fundamentally ignore what the searcher wants. SEO writing begins with intent analysis, not just picking a high-volume keyword from a list. For example, if you are targeting “best running shoes for flat feet,” the user is looking for a comparison guide or a listicle. If you try to rank a single product page for that query, you are fighting a losing battle against the SERP (Search Engine Results Page).
You should also be wary of 3rd party keyword data. In my experience, these databases are often too small to represent real-time opportunities, and their search volume or competition metrics are frequently inaccurate. Instead of treating these numbers as absolute truths, I look directly at the search results. If the top 10 results for your target term are all informative blog posts, you must produce a blog post. If they are mostly category pages, you need to focus on optimizing your store’s taxonomy.
To avoid content cannibalization, where multiple pages on your site compete for the same keyword, we rely on what is keyword clustering to group terms by intent. This process allows you to target an entire group of related queries with one comprehensive piece of content. You can manage this manually for small sites, but for larger catalogs, I recommend using a free SERP-based keyword clustering tool to identify which keywords belong together based on real-world search result overlaps.
The ecommerce writing strategy for category growth
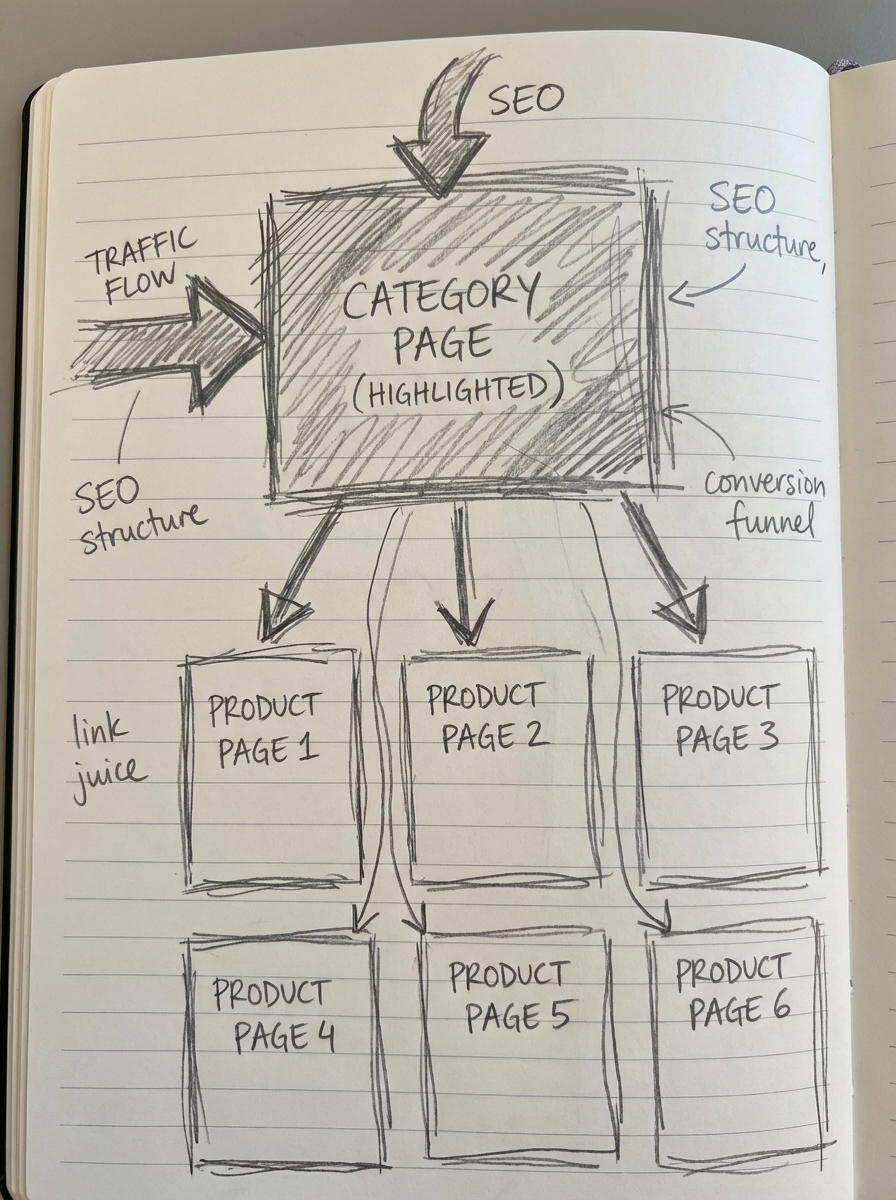
Most WooCommerce merchants make the mistake of over-optimizing individual product pages while neglecting their categories. I believe it is far more important to optimize category pages, as they drive the majority of transactional traffic. Data shows that well-optimized category pages can drive significantly more estimated traffic than individual product pages because they capture broader, higher-volume commercial keywords.
- Start with a content brief to ensure every piece of content has a clear roadmap before writing begins.
- Prioritize specific category names over vague ones to help buyers find products more easily.
- Use a free ecommerce category page optimizer to identify low-hanging fruit in your store’s structure.
A proper brief should define the target keyword, the primary intent, the required depth based on competitors, and a suggested heading structure. This prevents writers from simply “filling the page” and ensures the content serves a specific SEO purpose from the first draft.
Focus on above the fold value and structure
Modern searchers are impatient and often scan content for immediate answers. I always recommend an “answer-first” approach where you provide the core value proposition or the direct answer to the user’s query within the first 300 words. My research shows that links and information placed higher in the body of the text receive 37% more user clicks. This is why we prioritize WooCommerce internal linking within the introduction of our articles to move users deeper into the funnel quickly.
Your heading structure (H1, H2, and H3) acts as a skeleton that search engines use to understand the hierarchy of your information. The H1 should be reserved for your main title and include your primary keyword. H2s should represent the sub-topics or sections of your cluster, while H3s handle specific details or steps. By naturally incorporating long-tail keywords into these subheadings, you can capture highly specific, high-converting niche traffic that broad “head” terms might miss.
Effective SEO writing for WooCommerce must also bridge the gap between information and commerce. We use WooCommerce topic clusters to link informational blog posts back to transactional category pages. This structure establishes topical authority and guides the user through the entire buyer journey, from initial research to the final purchase.
Technical essentials for on-page performance
Writing high-quality text is only half the battle; the content must be supported by a solid technical foundation. Internal linking is arguably the most underrated lever in ecommerce SEO. Your blog posts should link to your category pages, and those categories should link back to your top-performing products. This distributes PageRank throughout your site and helps search engines index your catalog more efficiently.
Implementing structured schema markup – such as Article, FAQ, or Product schema – is another non-negotiable step. This metadata helps search engines interpret your content more accurately and can increase your click-through rate from search results by 30% through rich snippets. Every page should also pass through a rigorous content quality assurance process to verify factual accuracy, brand voice consistency, and technical elements like meta descriptions and alt text.
A systematic on-page SEO process ensures that you aren’t just publishing content, but actually optimizing it for visibility. This includes managing URL structures, page speed, and mobile responsiveness, which are critical for maintaining rankings in an increasingly mobile-first search landscape.
Iterating with AI and automation
I treat SEO content like a product: it requires constant iteration. You do not need a 5,000-word masterpiece on day one. I suggest launching a “Minimum Viable Product” version of your article quickly and then improving it once it shows signs of gaining organic traction. AI has fundamentally disrupted this process by making optimization significantly cheaper. While some fear the impact of AI on search, the efficiency it provides for research and drafting currently outweighs the risks.

You can use a free AI SEO content writer to handle the initial heavy lifting of research and formatting. The key is to maintain human oversight for brand voice and factual verification while letting the AI manage the grunt work. For stores with large catalogs, manual SEO writing is simply not scalable. We built ContentGecko to automate this, providing catalog-aware blog content that stays in sync with your live inventory, pricing, and stock levels.
Regularly performing SEO content audits will help you identify which of your automated or MVP pages are performing best. This allows you to allocate your manual optimization resources to the pages that have the highest potential for driving revenue, ensuring your SEO strategy remains both efficient and profitable.
TL;DR
SEO writing is a systematic process of aligning content with search intent and site architecture. For ecommerce brands, the highest ROI comes from optimizing category pages over individual products and using SERP-based clustering to group keywords accurately. You should focus on providing value “above the fold,” maintaining a strict QA process, and using automation to scale content production. Start by launching content quickly, then use audits to refine and optimize the pages that show the most promise.
