Real-world case studies of businesses succeeding with LLMs and GenAI
Generative AI has moved beyond experimentation into production-ready workflows that drive measurable revenue. For WooCommerce marketers and SEO leads, the shift toward large language model optimization represents the first major change in search behavior since the move to mobile. Companies successfully navigating this shift are no longer just “using ChatGPT”; they are restructuring their entire content architecture to be machine-readable and intent-aligned.
B2B SaaS: 43% traffic growth through Q&A restructuring
I have observed that many B2B companies struggle with content that is heavy on thought leadership but poor for search visibility. One B2B SaaS platform addressed this by completely overhauling its content format to align with how LLM search engines retrieve information. They shifted from traditional long-form blog posts to a conversational, question-and-answer structure.

By converting product documentation and feature pages into direct questions and answers – such as “How does our product integrate with AWS?” instead of “Cloud Integration Features” – they saw a 43% increase in organic traffic within three months. This occurred because AI agents like Perplexity and Google’s Gemini could easily extract direct answers to serve in AI Overviews and generative summaries. This transformation involved several technical adjustments:
- Implementing comprehensive FAQ schema to signal clear answers to crawlers.
- Restructuring H2 and H3 headings as natural language questions.
- Standardizing entity naming across the site to avoid confusing the model.
Ecommerce: 25% traffic boost via entity-centric optimization
In my experience, the most common mistake WooCommerce stores make is ignoring the relationship between entities. One ecommerce retailer specializing in athletic footwear moved away from thin product descriptions and focused instead on “entity-centric” clustering.
Instead of just trying to rank for a single brand name like “Nike Air Max,” they built comparison hubs like “Nike Air Max vs. Adidas Ultraboost for Marathon Training.”
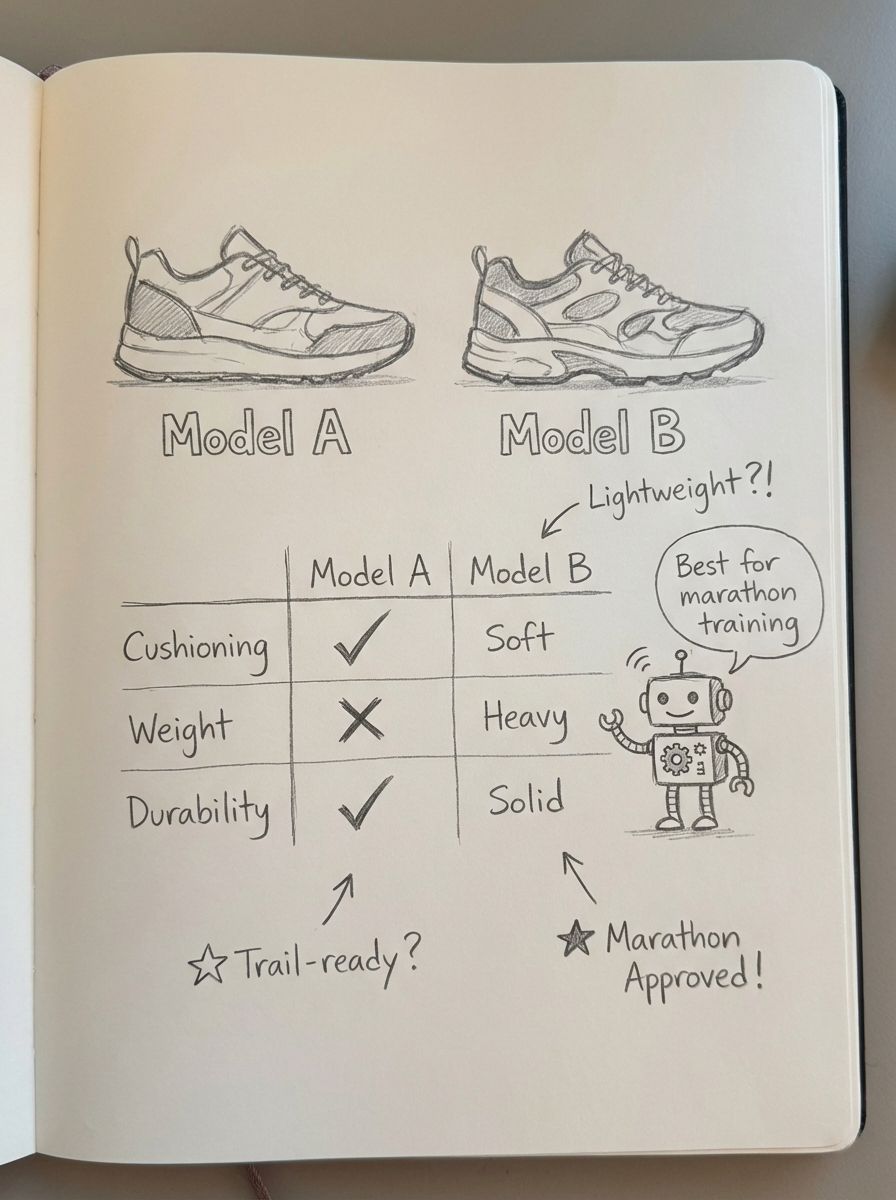
This strategy treats content like a product, where you launch an MVP version of an AI-generated article and then iterate on it based on actual traffic performance.
The result was a 25% increase in organic traffic and a significant rise in visibility for generative shopping recommendations. By providing the “why” behind product features – such as explaining why a specific foam density matters for flat-footed runners – they fed the LLMs the context needed to recommend their products in conversational queries.
Scaling production: 70% reduction in content creation time
Scaling a blog for a store with 10,000 or more SKUs used to be a multi-year project. We have seen firms use AI-powered automation to reduce content creation time by 50% to 70%. One retailer cut their production cycle from three weeks to just four days while maintaining high editorial standards.
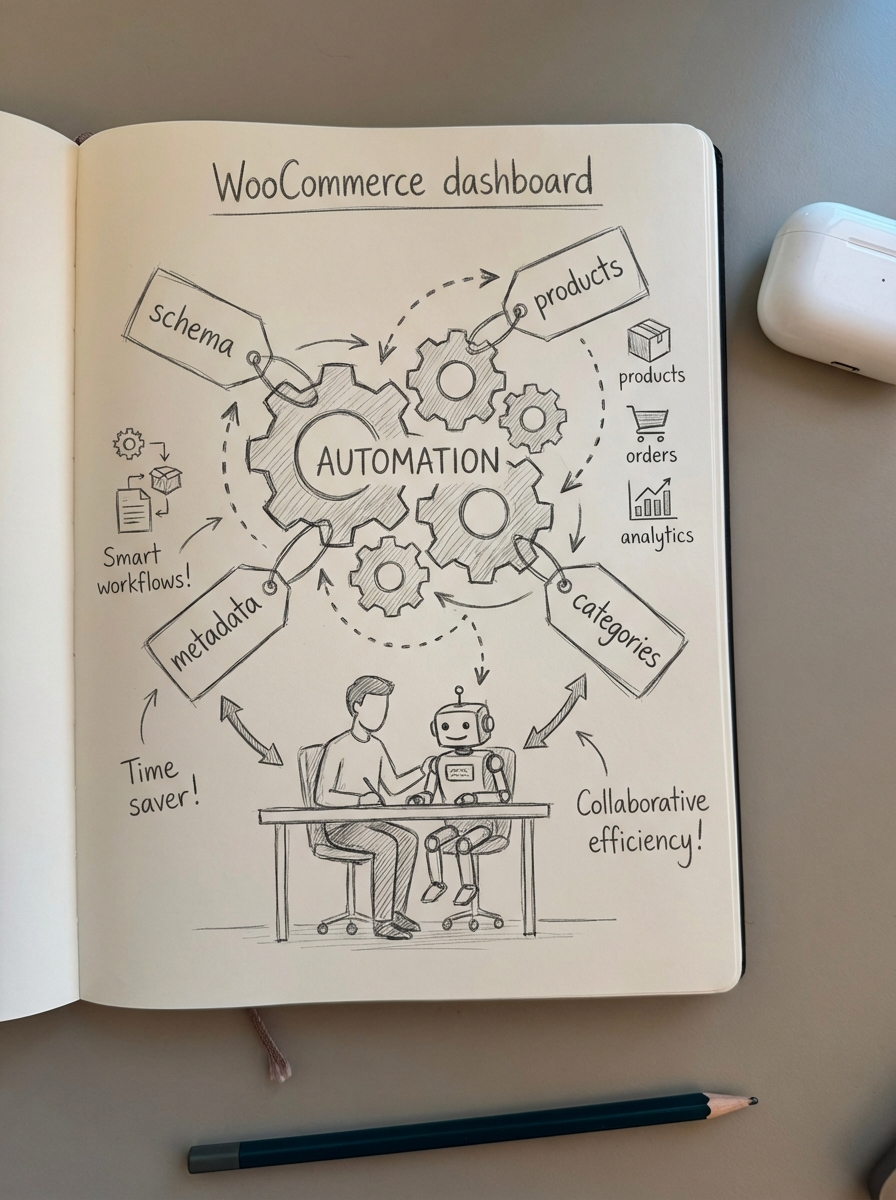
The key lesson here is not to automate the entire process blindly but to use AI for the “labor” of content preparation. These successful brands use AI to handle SERP-based keyword clustering to avoid keyword cannibalization. They also generate first drafts based on specific WooCommerce catalog data and automatically update content when prices or stock levels change.
This is a core capability we built into ContentGecko. Research shows that marketing teams using these automated workflows report significant increases in organic rankings because they can maintain a much higher content update frequency than manual teams can achieve.
Financial services: 90% answer accuracy through structured metadata
A financial services firm faced a high “hallucination” rate when their internal AI agents tried to answer customer queries. They solved this by improving their metadata strategy. By adding structured URL metadata and tagging content with audience markers – such as identifying a page as “educational” for “first-time homebuyers” – they improved answer accuracy from 67% to over 90%.
This highlights a contrarian truth: the first step in optimizing for AI is getting the traditional technical SEO basics right. If your site architecture is bloated or your data is not structured, an LLM will struggle to parse your authority regardless of how sophisticated the model is.
Beauty and retail: 35% lift in repeat purchases
One beauty brand used GenAI to implement one-to-one personalized content journeys. By using LLMs to analyze customer reviews and turn that unstructured feedback into structured, AI-usable data, they created buyer guides that felt hyper-relevant to specific skin concerns.
The result was a 35% lift in repeat purchases. They were not just writing blog posts; they were using GenAI to map user intent more accurately across the entire funnel. This type of implementation ensures that when a user asks an AI assistant for a recommendation, the brand’s specific use cases and customer outcomes are already part of the model’s knowledge graph.
Pragmatic lessons for WooCommerce operations
If you are managing a WooCommerce store, these case studies suggest three immediate actions to future-proof your traffic.
It is way more important to optimize category pages than product pages. Most ecommerce sites have thin category pages, but successful brands are turning these into educational hubs with embedded buying guides and comparison matrices to satisfy generative engine optimization requirements.
You should use a hybrid workflow rather than replacing your writers entirely. Use LLMs to handle the research and drafting, and keep humans in the loop for strategy and brand voice. Tools like ContentGecko allow you to ingest your unique style guide so the output does not sound like generic AI fluff.
Finally, automate your metadata wherever possible. Nobody should be writing meta descriptions by hand in 2026. Use that saved time to focus on schema markup and internal linking structures that help AI crawlers build a clear map of your site’s expertise.
TL;DR
Real-world success with GenAI requires moving from “chatting” to “structuring.” Case studies show that restructuring content into Q&A formats can drive a 43% traffic increase, while entity-centric clustering for ecommerce can boost visibility by 25%. The path to a high ROI in LLM optimization involves automating production to save up to 70% of your time while doubling down on technical foundations like schema and metadata to ensure AI agents can accurately retrieve and cite your brand.
