Traditional SEO vs. LLMO: How to optimize for both worlds
Optimizing for AI answer engines like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overviews begins with mastering traditional SEO fundamentals. Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) is not a replacement for classic search engine optimization; it is an evolution in how we structure and present information for machine synthesis. If your technical foundation is broken or your topical authority is nonexistent, an LLM will not cite you, and a traditional crawler will not rank you.
I have spent years watching search engines move from simple pattern matching to deep semantic understanding. LLMO – frequently referred to as Generative Engine Optimization – is simply the next layer of that stack. While traditional search provides a list of links, LLM-based search engages users in a dialogue, directly comparing products and anticipating follow-up questions. For WooCommerce merchants, the goal is to remain visible in both the link-heavy SERPs and the conversational outputs of AI assistants.

Understanding the shift from keywords to intent
Traditional SEO has long relied on keyword density and backlinks to signal relevance. In contrast, large language model optimization shifts the focus toward semantic relevance and citation potential. LLMs do not just look for a string of text; they identify comprehensive answers that satisfy a specific user intent. We are seeing search queries grow up to four times longer than they were previously, signaling a definitive shift from short keywords to natural language questions.
Consider the user intent behind a search for “best ergonomic chairs.” In a traditional environment, Google returns a list of affiliate guides and product pages. In an AI-driven environment, a user might ask, “Which ergonomic chair is best for lower back pain under $500?” The AI synthesizes a specific answer based on technical specs and usage data. Research indicates that shoppers engaging with AI-powered assistance are 25% more likely to convert because the AI effectively handles the product validation phase of the buyer journey. To win the citation, your content must be “synthesizable” – if an AI cannot easily extract facts, comparisons, and specs from your page, your brand will be left out of the answer.
The technical foundation: Schema and architecture
For an LLM to retrieve and process your data effectively, it requires explicit structure. While traditional SEO uses XML sitemaps to guide crawlers, LLMO relies heavily on structured schema markup and a highly organized semantic website architecture. I believe many ecommerce sites over-complicate their technical stack when they should be focusing on cleaning up their existing data signals.
Schema acts as the API for LLMs. By using Product, FAQ, and Review schema, you provide the explicit signals that AI engines need to parse your offerings without “guessing” the context. Beyond the code, you must flatten your site architecture. LLMs favor thematic clusters that demonstrate deep topical authority. We utilize a pillar-and-cluster approach to ensure related concepts are tightly linked, making it easier for AI crawlers to build a comprehensive knowledge graph of your store. With zero-click searches representing roughly 60-65% of all queries, you must position yourself as the authoritative source that the AI displays, even if the user never clicks through to your site.
Why category pages are your strongest LLMO asset
A common mistake among ecommerce marketers is spending excessive time on individual product pages while neglecting category pages. Product pages are volatile; SKUs go out of stock, prices change, and URLs are often removed. Category pages, however, are permanent fixtures of your topical authority. For an LLM, a well-optimized category page serves as an information hub that connects broad intent to specific solutions.
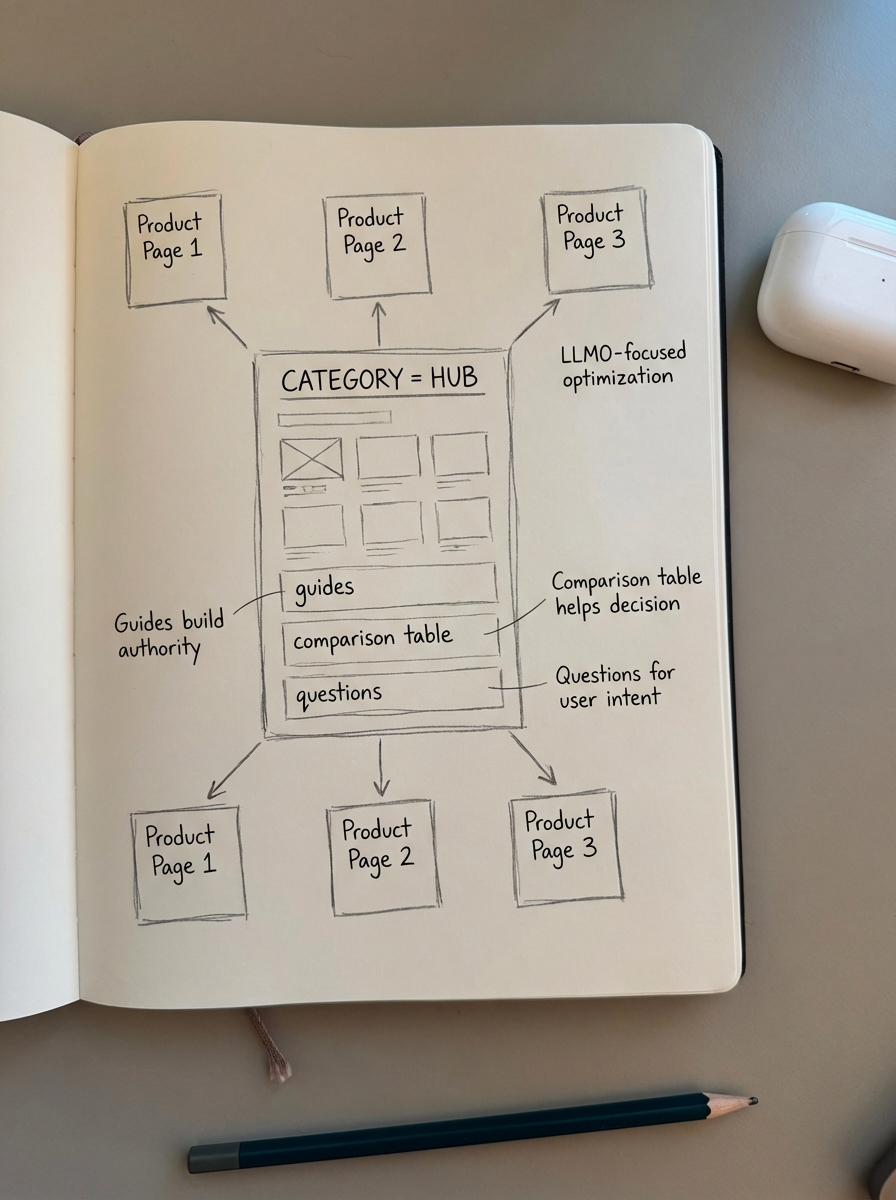
Most ecommerce sites use vague category names that offer little semantic value. To perform well in AI search, your category pages should function as educational guides rather than simple product grids. I recommend including:
- Comprehensive buying guides that explain spec variations.
- Data-rich comparison tables for top-selling models.
- Specific usage scenarios and compatibility notes.
- Clear headers that answer common customer questions.
If you are unsure whether your current structure is too generic, our free ecommerce category optimizer can identify where your category names lack the specificity required for both Google and AI engines to understand your catalog hierarchy.
Content strategy: From SEO fluff to citation-worthy facts
The era of “thought leadership” fluff is over. AI models are trained to prioritize factual accuracy and Expertise, Authority, and Trust (E-A-T). Traditional SEO content often focused on word count to hit keyword targets, but LLMO demands high “citation potential.” Over 70% of shopper queries now focus on validation – compatibility, technical specs, and real-world usage – rather than generic brand awareness.
To adapt, we have shifted our AI SEO content writer to prioritize conversational formatting. This involves structuring articles with questions as headers followed by immediate, direct answers. This dual-structured approach makes it easier for AI Overviews to “scrape” and feature your content as the primary answer. If your goal is to capture ChatGPT traffic, you must provide specific, verifiable facts that the model can cite as evidence for its recommendations.
Measuring performance in the AI era
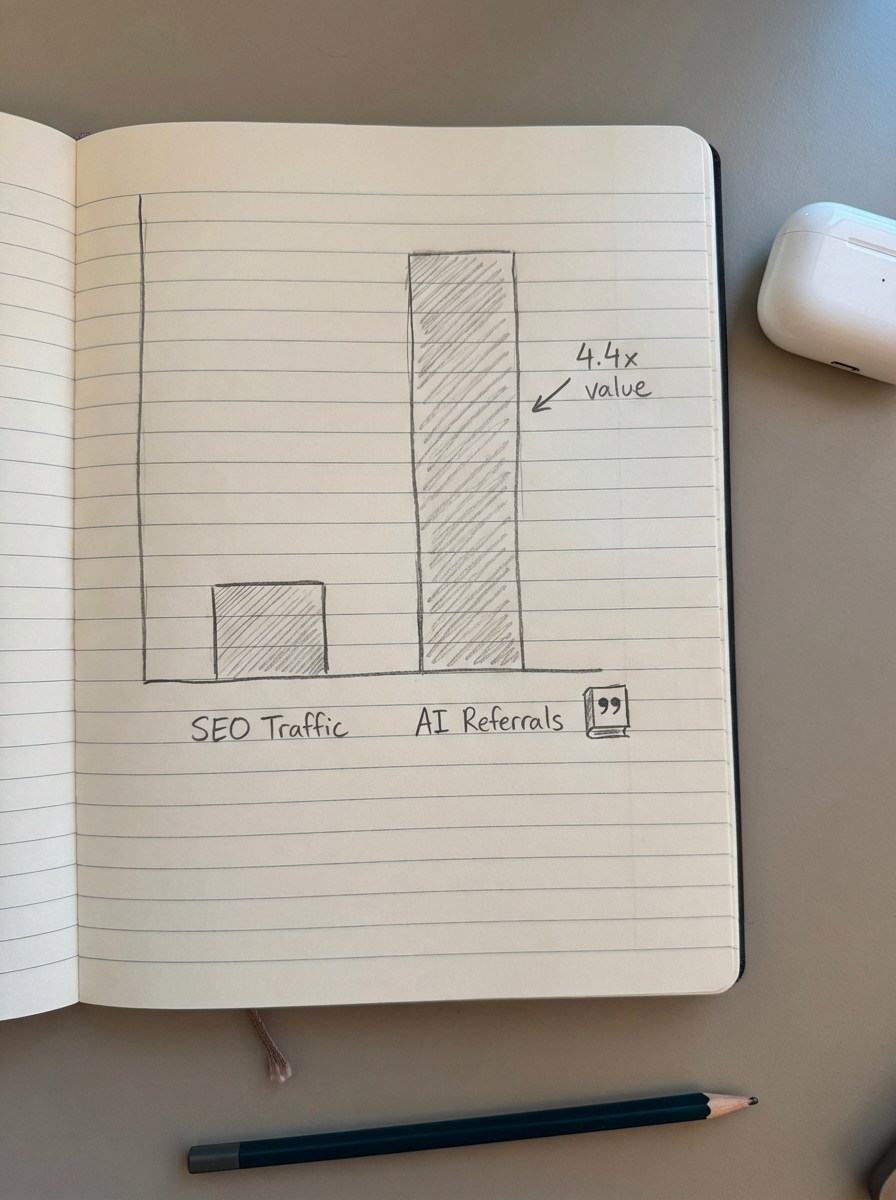
Standard metrics like average position are becoming increasingly irrelevant in a world of personalized, dynamic AI responses. While AI referral traffic currently benchmarks at a modest 1.08% of total site traffic, these visitors are often up to 4.4 times more valuable. They have already been vetted by the AI assistant, meaning they arrive at your site with higher intent and a higher likelihood of conversion.
I suggest using an ecommerce SEO dashboard that segments performance by page type. This allows you to verify if your blog is driving awareness through AI citations while your category pages maintain their rankings in traditional search. Stop worrying about meta descriptions; by 2026, Google and most LLMs will be rewriting them entirely to fit the user’s specific prompt. Instead, focus on monitoring LLMO performance by tracking your citation frequency and the “synthesizability” of your content across different LLM platforms.
TL;DR
- Foundation First: You cannot optimize for AI if your traditional SEO foundations – speed, crawlability, and schema – are broken.
- Keywords to Intent: Shift your focus from high-volume head terms to answering complex, natural language questions that shoppers actually ask.
- Prioritize Categories: Category pages provide more stable, authoritative signals for LLM knowledge graphs than volatile product pages.
- Be Citation-Ready: Use clear H2/H3 hierarchies, comparison tables, and factual data segments to make your content easy for AI to cite.
- Adopt New Metrics: Track AI-specific conversion paths and citation frequency, as AI-referred visitors often demonstrate significantly higher average order values.
