Practical large language model optimization for ecommerce
Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) is the immediate successor to traditional technical SEO, shifting the focus from ranking blue links to ensuring your product catalog is the primary data source cited by generative engines. For WooCommerce merchants, the objective is to become the definitive reference for platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews.
The strategic shift to category-level LLMO
I have long argued that optimizing category pages is significantly more important than optimizing individual product pages. While product pages target specific SKUs, category pages capture broader, high-volume transactional intent. In the era of LLM search, this remains true because generative engines are built to synthesize information. They are far more likely to recommend a curated list of products derived from a well-optimized category page than to surface a single, isolated product in a vacuum.
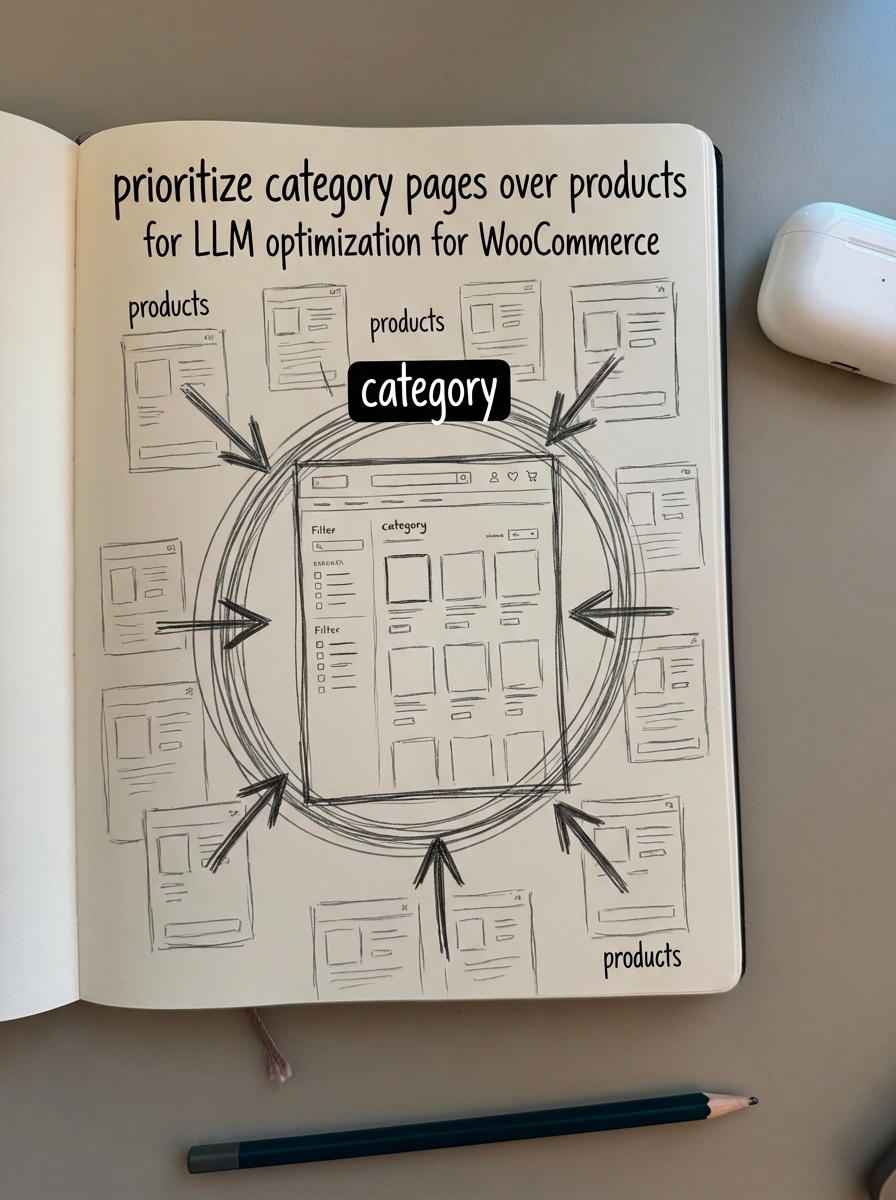
Industry data supports this shift, showing that 58% of consumers now use generative AI for product recommendations, representing a massive jump in adoption. If your category pages are not structured to be retrieval-friendly, your brand is essentially invisible to these users. We are moving away from traditional keyword density toward a framework defined by semantic relevance and entity recognition.
Building effective prompt patterns for ecommerce content
The biggest mistake I see in ecommerce AI workflows is a lack of context. AI typically only hallucinates when your prompt is missing the necessary boundaries and data points. To produce high-quality category copy or buyer guides that actually drive conversions, you need a structured prompt architecture that provides the model with the exact parameters of your business.
We utilize a “Context-Task-Constraint” framework to anchor our outputs in reality. In this workflow, you define the role as a senior ecommerce merchandiser and provide the full category hierarchy along with top-selling SKUs and unique selling propositions. For the task itself, you can use our free ecommerce category optimizer as a baseline for title suggestions. Finally, you set constraints to avoid generic marketing fluff and require the inclusion of technical comparison tables. By providing the LLM with your actual product data, you eliminate the risk of the model recommending out-of-stock items or hallucinating specifications.
Retrieval-augmented generation for catalog accuracy
For a WooCommerce store managing thousands of products, you cannot fit your entire catalog into a single prompt window. This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) becomes the essential bridge between your store and the model. RAG allows the model to look up specific data from your store in real-time before generating content, ensuring accuracy.
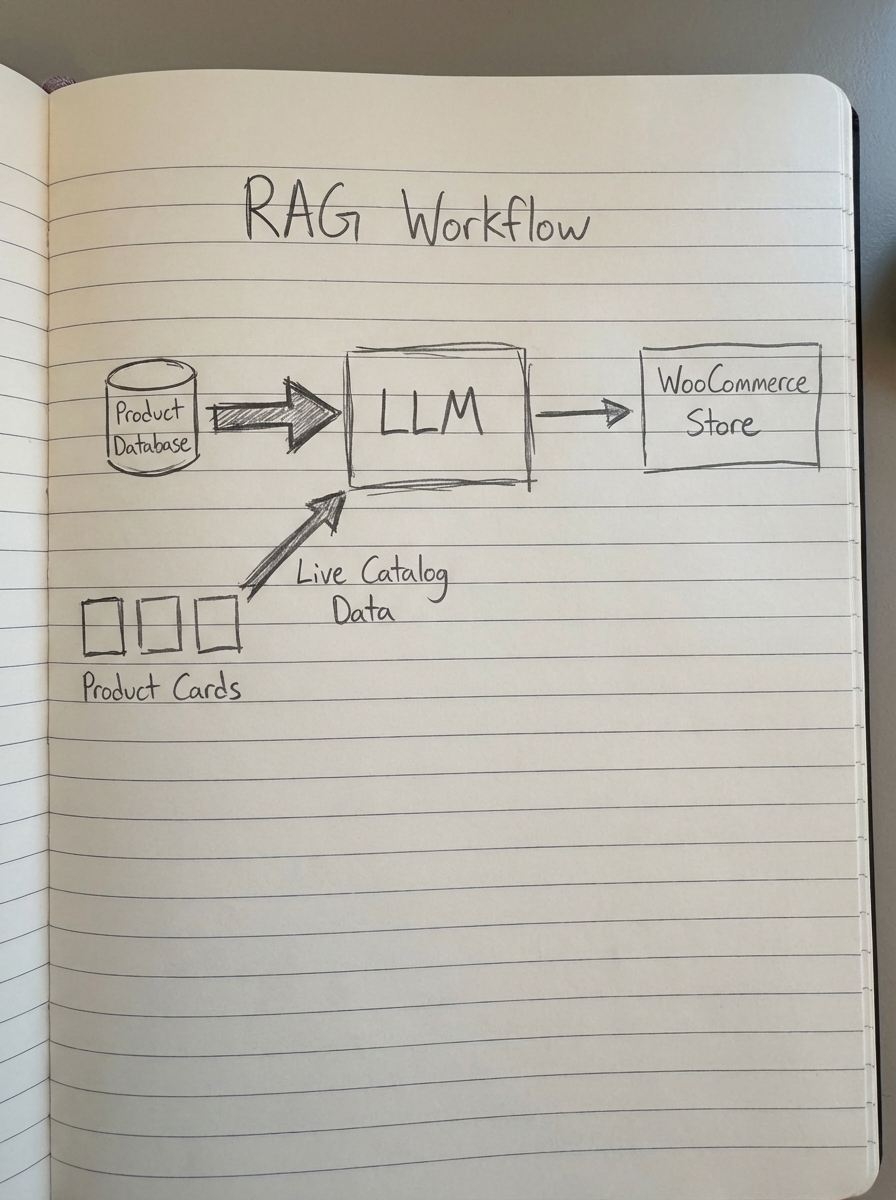
To make RAG effective, you must focus on structuring data for LLM retrieval through several technical layers. Vector embeddings are used to convert product descriptions into numerical representations that reflect conceptual meaning, while metadata enrichment involves tagging products with use cases and compatibility markers. Furthermore, a comprehensive schema strategy – including FAQ, Product, and Category schema – explicitly signals your data structure to AI crawlers.
At ContentGecko, we facilitate this through catalog-synced workflows that ensure the content published to your blog or category pages always reflects your current inventory, pricing, and URLs. This removes the manual burden of updating content every time a price changes or a SKU goes out of stock.
Fine-tuning versus prompt engineering for brand voice
A common objection to AI-generated content is that it sounds robotic. While prompt engineering handles the vast majority of use cases, fine-tuning is the specialized solution for the remaining edge cases where brand voice is paramount. Fine-tuning involves training a model on your specific customer service transcripts and high-performing historical content.
However, for most growing WooCommerce stores, scaling content updates with AI assistance through style guide ingestion is more cost-effective. You can feed your specific brand style guide directly into the LLM as a system message to ensure a consistent tone across hundreds of category descriptions. This approach can also reduce token usage by 30-40%, lowering your operational costs while maintaining high-quality output.
Evaluating LLMO performance and citation rates
You cannot manage what you do not measure, and the KPIs for AI search differ from traditional SEO. While we still care about traffic, we now have to track AI citation frequency and retrieval rates to understand our visibility within generative engines. If your content isn’t being cited, it usually indicates that your on-page SEO process lacks the conversational formatting or structured data these engines prefer.
I recommend implementing a multi-stage content quality assurance process to maintain high standards. This should include automated fact-checking using tools like Perplexity or DeepSeek R1 to verify technical claims. You must also ensure intent alignment, checking that the generated content actually answers the questions users are posing in AI search queries. Monitoring how often your brand appears as a source in ChatGPT or Google’s AI Mode is the new standard for measuring authority.
Integrating LLMO into your WooCommerce workflow
LLM optimization is the great equalizer in ecommerce. Small companies can now perform like enterprise giants by adopting these automated workflows early and bypassing the need for massive content teams. Using the ContentGecko ecommerce SEO dashboard, you can monitor how your category pages perform across both traditional search and AI-driven platforms simultaneously.
The first step is always getting the foundational architecture right. If your WooCommerce topic clusters are well-structured and your categories are clearly named, you have already done half the work required to feed the LLMs. From there, it is a matter of syncing your data and letting the models work for you.
TL;DR
- Prioritize category pages over product pages to capture high-volume transactional intent that LLMs prefer for synthesis.
- Use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) instead of relying solely on fine-tuning to ensure your content uses live, accurate catalog data.
- Implement semantic metadata and comprehensive schema markup to make your content easy for generative engines to retrieve and cite.
- Shift your performance tracking toward AI citation rates and referral traffic from generative engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity.
- Automate your content pipeline with platforms like ContentGecko to sync your product inventory with your SEO strategy for zero-maintenance growth.
