LLMO challenges for multinational websites
Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) for multinational ecommerce stores is significantly more complex than standard SEO because you are no longer just managing keyword rankings; you are managing cross-lingual context retrieval. If your WooCommerce store operates across multiple regions, your biggest challenge is ensuring that LLMs accurately associate your specific regional products with the correct local user intent.
The curse of multilinguality in AI retrieval
In my experience, the most overlooked hurdle in global LLMO is the “curse of multilinguality.” While LLMs are impressive polyglots, their training data is heavily skewed toward English. This creates a performance gap where an AI model might perfectly understand your product utility for a US audience but hallucinate or fail to retrieve your content for a Finnish or Slovak user because the underlying data density is lower.
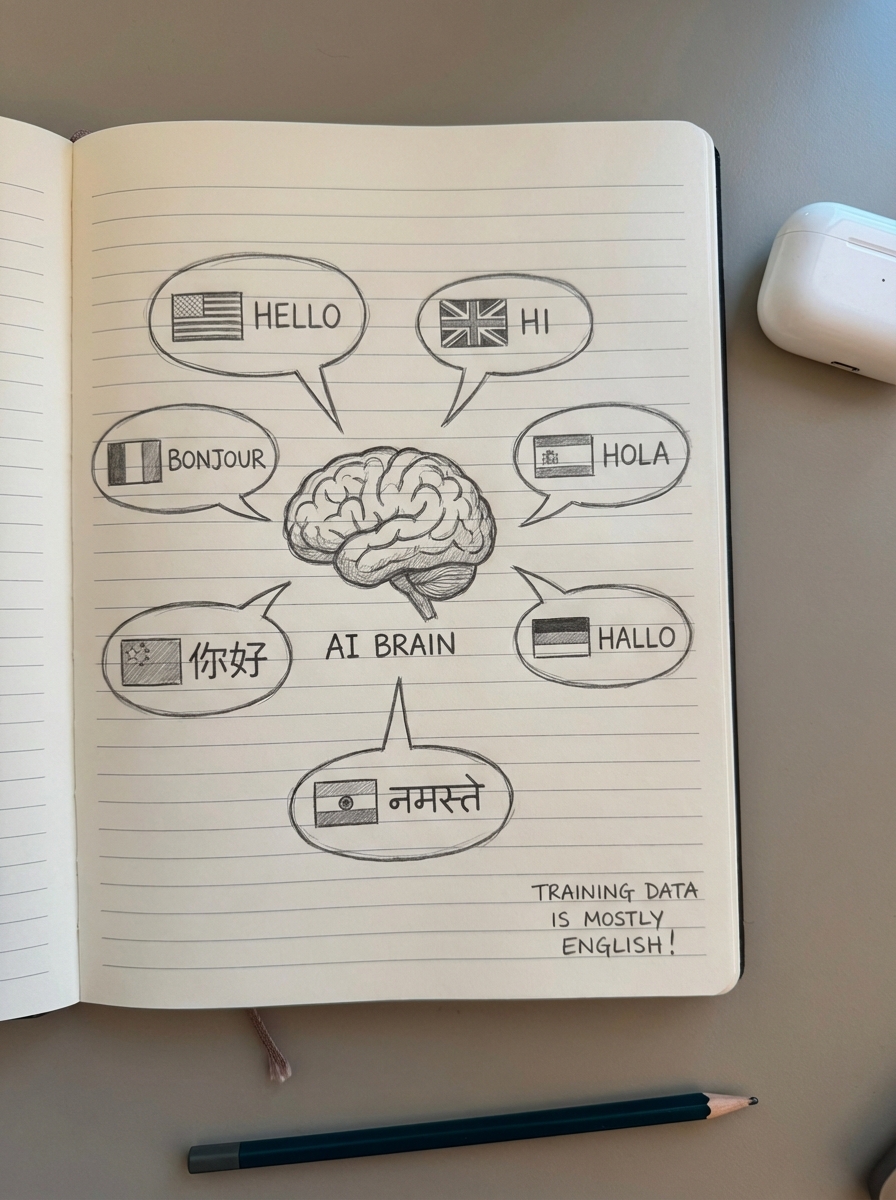
When an LLM retrieves information to answer a prompt – a process often involving Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) – it relies on structuring data for LLM retrieval that matches the user’s linguistic and cultural context. If your localized content is a thin, literal translation of your English site, it likely lacks the semantic markers needed for the LLM to verify your authority in that specific local market. I have seen countless brands lose visibility because they treated translation as a mechanical task rather than a contextual one.
Hreflang and geo-targeting as retrieval signals
A common mistake I see among multinational brands is assuming that LLMs ignore traditional technical signals like hreflang. In reality, comparing traditional SEO and LLMO techniques reveals that the first step in optimizing for AI search engines is getting traditional SEO right. Most websites currently have missing or broken hreflang setups, which creates immediate friction for AI crawlers trying to map content to specific regions.
LLMs use your site’s technical architecture to disambiguate which version of a page should be cited. If your implementation of WooCommerce international SEO strategy is inconsistent, an LLM might serve a UK user a product recommendation from your US store. This leads to incorrect pricing, out-of-stock errors, and a fragmented user experience.
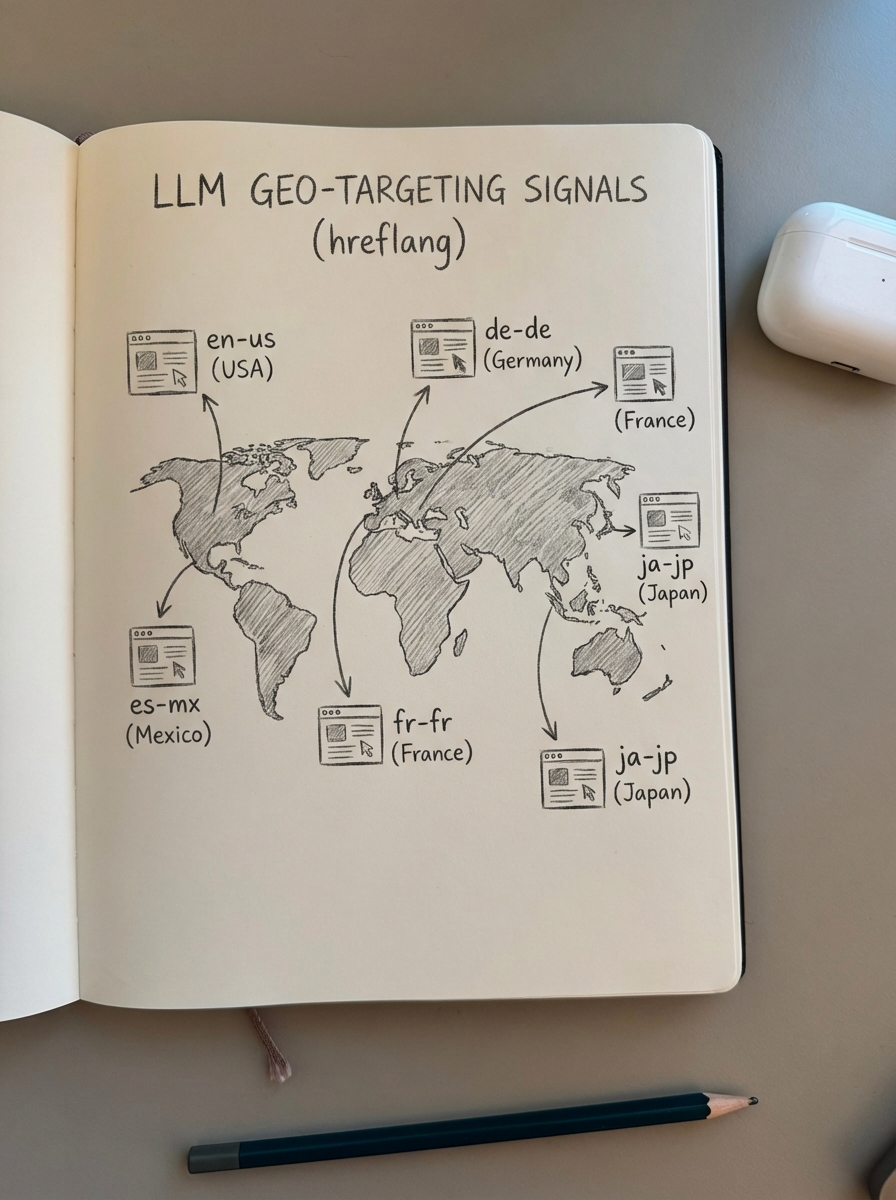
To ensure global discoverability, your technical foundation must include:
- Bidirectional hreflang tags to signal language and regional variants clearly to AI crawlers.
- Region-specific schema markup as part of your effective metadata strategies for LLMO.
- Standardized URL structures that help LLMs build a more robust knowledge graph of your entire global brand.
I generally recommend subfolders over subdomains for consolidating authority. Diluting your SEO equity across multiple “authority accounts” makes it harder for LLMs to recognize your domain’s global reach. You can find a deeper breakdown of this in our guide on subdomains vs. subfolders.
Catalog complexity and regional hallucination risks
Managing a global WooCommerce catalog with thousands of SKUs introduces significant “hallucination” risks. An LLM might correctly identify that you sell “waterproof hiking boots” but incorrectly claim they are available in your German store when they are actually only in stock in France. This happens because LLMs often struggle with real-time data accuracy across fragmented regional databases.
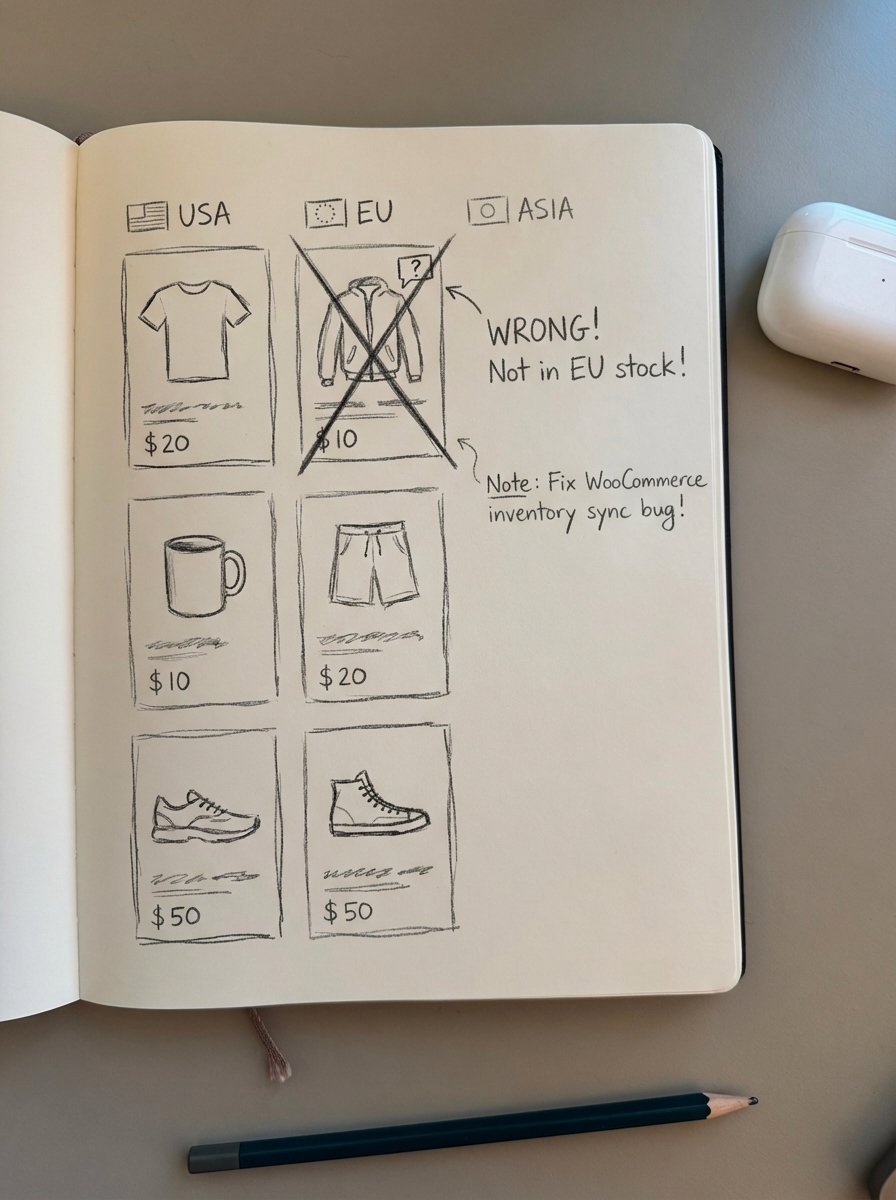
I believe the only way to solve this at scale is through a catalog-synced content strategy. By feeding LLMs structured data that is tied directly to your live inventory, you reduce the likelihood of the AI providing inaccurate regional information. At ContentGecko, we address this by using our WordPress connector plugin to ensure that every piece of blog content produced is aware of the specific SKU availability, pricing, and currency for that region. This turns your blog from a static asset into a live data source that AI agents can trust.
Moving beyond literal translation to semantic localization
For an LLM to cite your brand as an authority, your content must reflect local semantic intent. A user in the UK searching for “trainers” has a different intent profile than a US user searching for “sneakers,” even if the product is identical. Literal translations fail LLMO because they miss the conversational nuances that LLM-based search prioritizes.
If your blog content doesn’t answer local questions using the specific phrasing and cultural context of that market, it won’t be retrieved as a top-tier source. I advocate for adapting website architecture for LLM search by clustering content around local problems rather than just translated keywords. This ensures that when a user asks an AI agent a complex question, your brand’s local expertise is the one being quoted.
How ContentGecko simplifies global LLMO
Scaling a manual content team to handle multilingual LLMO challenges is prohibitively expensive for most multinational brands. The overhead of maintaining brand consistency, technical accuracy, and regional relevance across dozens of markets usually leads to “content rot” – where outdated information stays live and confuses both users and AI agents.
ContentGecko solves this by automating the production of a catalog-synced, AI-optimized blog that handles the heavy lifting for you. We sync with your regional WooCommerce catalogs to ensure price and stock accuracy in every article and automate the deployment of hreflang and schema to reduce the technical lift for your SEO team.
Using our ecommerce SEO dashboard, you can track how your pages perform across different segments. This allows you to identify which regional content is successfully capturing AI citations and which areas need further optimization. By treating content as a live product that iterates based on regional data, you can stay ahead of the shift toward generative search without increasing your headcount.
TL;DR
Multilingual LLMO requires a shift from keyword-based translation to context-based retrieval. The core challenges – technical signal conflicts, training data imbalances, and catalog hallucinations – can only be solved by a technical foundation of strong traditional SEO combined with automated, catalog-aware content production. Use structured data and localized semantic clusters to ensure AI models see your brand as the global authority in every market you serve.
