WooCommerce international SEO
International expansion separates stagnant stores from high-growth operations. WooCommerce stores targeting multiple countries need to solve three concurrent challenges: making content discoverable in local search engines, providing a localized shopping experience, and handling cross-border logistics without breaking the site’s technical infrastructure.
The opportunity is significant. WooCommerce powers approximately 4.6 million stores worldwide and supports 118 languages out of the box, but most merchants never leverage this capability properly. The technical debt from a poorly executed international rollout – duplicate content penalties, crawl budget waste, conversion friction – compounds quickly.
Market selection and prioritization
Start with data, not assumptions.
The United States leads WooCommerce adoption with 422,024 stores, followed by the UK (170,832), India (131,682), and Canada (73,813). For US merchants, Canada represents the highest ROI first expansion – minimal language barriers, similar regulations, shared payment infrastructure.
Use your existing analytics to identify organic international interest. Filter Google Search Console by country, segment Google Analytics traffic by region, and review checkout abandonment by location. If you’re getting 500+ monthly organic visitors from Germany but no conversions, you have validation for expansion paired with a localization gap to fix.
Don’t expand to five countries simultaneously. The operational complexity will destroy your team. Pick 2-3 markets maximum for your first wave, validate product-market fit and localization effectiveness, then scale.
URL structure and site architecture
Three options exist for international WooCommerce sites: subdirectories, subdomains, or country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs).
Subdirectories (example.com/de/, example.com/fr/) consolidate domain authority and simplify management. This is the approach I recommend for 90% of WooCommerce stores. Airbnb scaled internationally using subdirectories without fragmenting their SEO equity across multiple domains. Implementation is straightforward, hosting is centralized, and SSL management doesn’t multiply.
Subdomains (de.example.com, fr.example.com) provide clearer content separation and can run on different hosting infrastructure if needed. The tradeoff is diluted domain authority and more complex analytics configuration. Use subdomains when you need true technical independence between markets – different payment processors, separate inventory systems, distinct compliance requirements.
ccTLDs (example.de, example.fr) deliver the strongest geo-targeting signals and maximum local trust. They’re also the most expensive and operationally complex option. You’re managing multiple domains, fragmenting backlink equity, and dealing with country-specific registrar requirements. Reserve ccTLDs for mature international operations where brand localization justifies the overhead.
For URL slugs within each language version, translate them. Don’t use example.com/de/blue-shirt – use example.com/de/blaues-hemd. Localized slugs improve CTR and signal relevance. Most multilingual plugins handle this automatically once configured.
For a deeper exploration of URL architecture fundamentals that apply across all market implementations, review our guide on WooCommerce URL structure best practices.
Hreflang implementation for WooCommerce
Hreflang tags are non-negotiable for international WooCommerce stores. They prevent duplicate content penalties and ensure users see the correct language version.
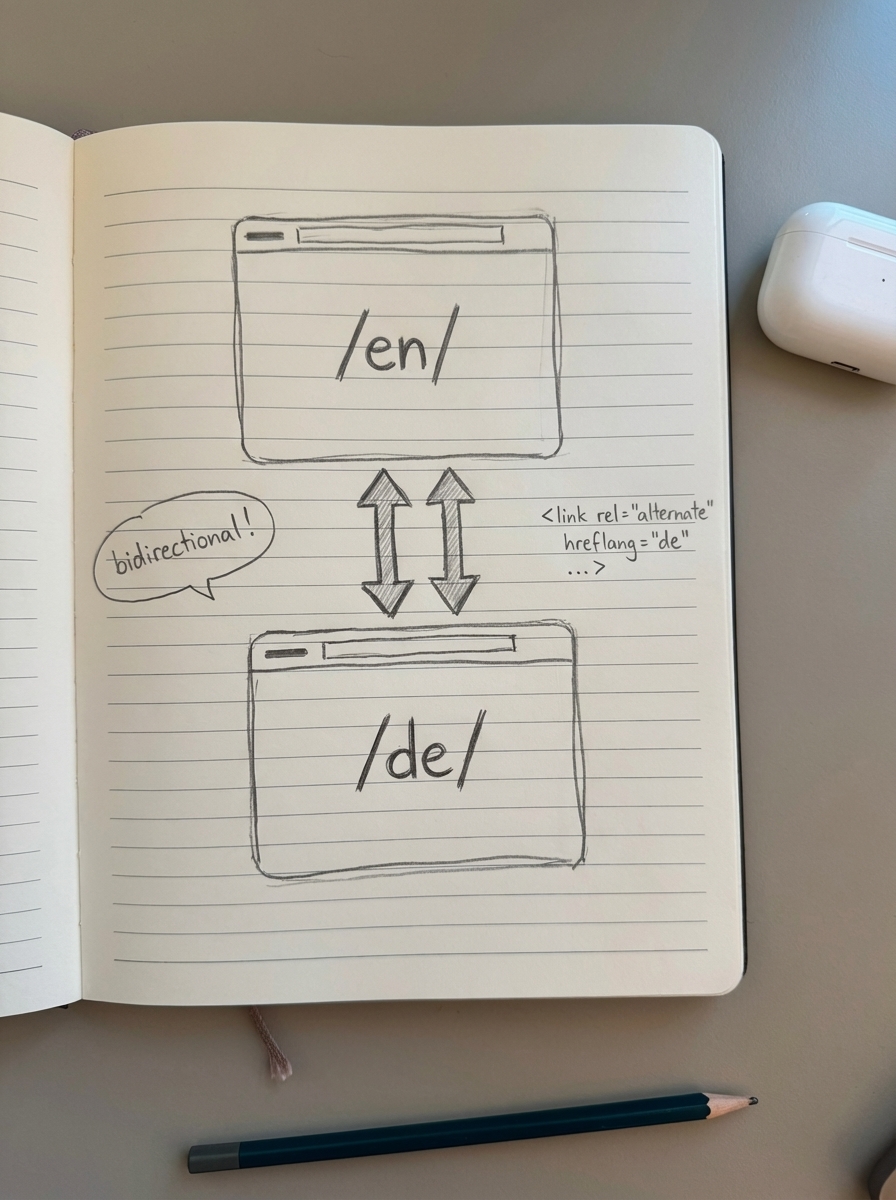
The implementation rules are strict. Every page needs self-referential hreflang. If example.com/de/product/ exists, it must include <link rel="alternate" hreflang="de" href="https://example.com/de/product/" />.
All language versions must link to each other bidirectionally. If your English product page links to the German version, the German page must link back to English. Missing reciprocal tags cause Google to ignore your hreflang entirely.
Use absolute URLs with protocol. Relative URLs break hreflang. Always specify https:// and the full domain.
Include an x-default tag for unmatched languages. This tells Google which version to show users when their language isn’t available: <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://example.com/en/product/" />.
Follow ISO standards exactly. Use en-gb not en-uk. Use pt-br not pt-BR. Google is particular about formatting.
For WooCommerce product variations, your hreflang strategy gets complex. Each product variation (color, size) shouldn’t have separate hreflang tags – those should canonicalize to the parent product. But each parent product should have hreflang pointing to its translated equivalents.
WPML and Polylang both handle hreflang generation automatically once configured. Validate implementation using Google Search Console’s International Targeting report and run regular crawls with Screaming Frog to catch reciprocal link errors.
For detailed technical guidance on the mechanics of hreflang, see our hreflang implementation guide and broader international SEO setup documentation.
Multilingual content and plugins
Translation is not localization. Running product descriptions through Google Translate creates content that ranks poorly and converts worse.
True localization requires market-specific keyword research. “Running shoes” in English might translate to “Laufschuhe” in German, but Germans actually search for “Joggingschuhe” or “Sportschuhe” more frequently. Use Ahrefs or SEMrush with country-specific databases to find actual search terms.
Cultural adaptation matters beyond words. Payment methods vary – Germans expect Sofortüberweisung, Dutch buyers want iDEAL. Size charts need localization – US shoe sizes don’t match EU or UK. Return policies have different legal requirements by country.
Display reviews from local customers in their language. Show local delivery times, not US-based estimates. Use region-appropriate imagery.
For currency and pricing localization, don’t just convert USD to EUR at exchange rates. Research local pricing expectations, account for VAT differences, and round to psychologically appropriate price points.
For implementation, three plugins dominate WooCommerce multilingual setups. WPML (WordPress Multilingual Plugin) is the most comprehensive solution. It handles product translations, variable products, taxonomy translations, and currency switching. The downside is complexity and performance impact on large catalogs. Budget $600-$1200 for site licenses plus translation management credits.
Polylang offers a simpler, more lightweight alternative. It’s free for basic multilingual functionality with paid add-ons for WooCommerce support. Better performance than WPML but less extensive feature set. Good choice for stores under 5,000 products.
TranslatePress provides a visual translation interface – you translate content while viewing the actual page. More intuitive than WPML’s admin interface but limited in advanced features. Works well for smaller catalogs prioritizing ease of use.
For currency switching, pair your translation plugin with WooCommerce Multi-Currency or Aelia Currency Switcher. These handle automatic geo-detection, currency conversion, and localized pricing rules. Display prices in local currency before checkout, not as a surprise at payment.
ContentGecko integrates with WPML and Polylang to generate product-focused blog content in multiple languages simultaneously. Our WordPress connector plugin handles multilingual publishing automatically, ensuring supporting content matches your catalog in every target market.
Technical SEO considerations
International WooCommerce stores compound standard technical SEO challenges.
Canonical tag complexity multiplies. Each language version needs proper self-referencing canonicals. Product variations must canonicalize to parent products within their language version, not across languages. Category pages with filters need canonical rules that account for language parameters. For implementation details, read our WooCommerce canonical tags guide.
XML sitemaps require segmentation. Create separate sitemaps for each language version or use sitemap index files to organize by country. Google Search Console lets you submit multiple sitemaps per property. Include language-specific product pages and categories, exclude parameter-based duplicates. Learn more about WooCommerce XML sitemap optimization.
Structured data needs localization. Product schema must include currency, availability, and review aggregates in the local context. Organization schema should reference local business entities if you have regional offices. BreadcrumbList schema must use translated category names.
Site speed varies by geography. A store on US-based hosting loads quickly for American customers but slowly in Asia. Implement a CDN (Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, StackPath) to serve static assets from regional edge servers. Compress images (WebP format with fallbacks), enable browser caching, and consider regional hosting for high-volume markets.
Duplicate content risks escalate. WooCommerce already creates duplicate content through product variations, categories, tags, and filtered URLs. Add multiple languages and you’ve multiplied the problem. Implement robots.txt rules to block low-value parameter combinations, use noindex,follow meta tags on thin filtered pages, and maintain consistent canonicalization across all language versions. Our WooCommerce duplicate content guide covers prevention strategies.
Use our free ecommerce category optimizer to identify category naming improvements across language versions. The tool analyzes category specificity and suggests optimizations that work better for international search intent.
Localized product pages and category content
Product page SEO fundamentals don’t change internationally – unique descriptions, optimized images, proper schema – but execution requires local context.
Translate product titles for search intent, not literal meaning. A “Men’s Running Shoe” might be better titled “Herren Laufschuh für Marathon” in German to capture specific search behavior. Use keyword research tools set to target markets to find what local buyers actually type.
Rewrite product descriptions entirely. Don’t translate. German buyers care about TÜV certifications; US buyers don’t. French buyers expect detailed material composition; UK buyers want delivery speed guarantees. Adapt features and benefits to local priorities.
Localize product attributes and filters. Size systems differ (US vs EU vs UK). Color names vary culturally. Measurement units need conversion (inches to centimeters). Configure WooCommerce attributes per language version with locally appropriate values.
Adapt category descriptions to local search behavior. Your “Women’s Winter Coats” category in English might need completely different content structure for “Damen Winterjacken” in German because search intent and seasonal timing varies. Use our free SERP keyword clustering tool to analyze which keywords should map to the same category across languages.
Implement faceted navigation strategically. International stores multiply the already complex faceted navigation SEO problem. You don’t want to index every size/color/material combination in six languages. Read our WooCommerce faceted navigation SEO guide to learn which filter combinations deserve indexation and which should be blocked.
For detailed product page optimization tactics, review our WooCommerce product page SEO guide.
Cross-border shipping and tax configuration
Technical SEO excellence means nothing if international customers abandon at checkout because shipping costs are unclear or tax calculation fails.
Configure shipping zones properly. WooCommerce lets you define zones by country, state, ZIP code, or shipping class. Create zones for each target market with accurate carrier rates. Integrate real-time shipping calculation via plugins (ShipStation, Shippo, WooCommerce Shipping) so customers see actual costs before checkout.
Be transparent about customs and duties. Nothing kills international conversions faster than surprise fees at delivery. Display estimated customs charges on product pages for international buyers. Use Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) shipping when economically viable – customers pay all fees upfront, eliminating delivery surprises.
Handle tax correctly by jurisdiction. EU VAT rules differ from US sales tax. Some countries require tax-inclusive pricing displays, others mandate tax-exclusive. WooCommerce supports both. Configure per-country tax rates in WooCommerce → Settings → Tax, or integrate tax calculation services (WooCommerce Tax, Avalara) for automatic compliance.
Show estimated delivery dates, not just costs. “7-10 business days to Germany” converts better than vague “international shipping.” Calculate realistic delivery windows by destination and display them prominently.
Offer region-appropriate payment methods. Credit cards aren’t universal. PayPal dominates some markets. Klarna is expected in Scandinavia. iDEAL in Netherlands. Sofort in Germany. Research local payment preferences and enable relevant gateways.
Tax and shipping plugins I’ve seen work reliably: WooCommerce Avalara for automated tax calculation, ShipStation for multi-carrier management, WooCommerce Shipping for simplified USPS/DHL integration. Budget 2-3 hours for initial setup per market.
International content strategy and blog localization
Product pages alone won’t rank internationally. You need supporting content – guides, comparisons, how-tos – that targets informational keywords in local languages.
This is where most WooCommerce stores fail. They translate their English blog into German and French, wonder why traffic doesn’t grow, then abandon international content entirely.
The problem: you’re competing against native content creators who understand local search behavior, reference local brands and regulations, and write naturally in the target language.
The solution: create content specifically for local markets rather than translating existing content. Research local keyword opportunities using Ahrefs or SEMrush with country filters to find keywords your US content never targeted. Germans searching for “Welche Laufschuhe für Anfänger” want different content than Americans searching “best running shoes for beginners.”
Reference local competitors and comparisons. If you sell electronics in Germany, compare your products to MediaMarkt and Saturn, not Best Buy. If you’re entering the UK, reference Argos and John Lewis.
Address market-specific questions. UK buyers care about Brexit import implications. German buyers want to know about 14-day return rights. French buyers expect certain warranty provisions. Create content answering these specific concerns.
Link to localized product pages naturally. Your German blog post should link to /de/produkt/ URLs, not English product pages. Maintain consistent internal linking architecture within each language version.
ContentGecko automates international content creation for WooCommerce stores. We generate market-specific blog content in multiple languages simultaneously, maintain catalog awareness across all versions, and handle automatic publishing with proper hreflang and internal linking. Our AI SEO content writer understands product context and creates conversion-focused content that references your actual inventory.
For broader international content strategy thinking beyond WooCommerce-specific implementation, review our international SEO strategies guide.
Measurement and performance tracking
International SEO requires granular measurement. Aggregate metrics hide market-specific problems.
Segment everything by country and language. In Google Analytics, create separate views or use advanced segments to isolate performance by region. Track organic traffic, conversion rate, average order value, and revenue per country.
Monitor Search Console data by language version. Add separate properties for each subdirectory (example.com/de/, example.com/fr/) or use domain properties with page filtering. Track impressions, clicks, and average position by market to identify growth opportunities.
Watch for market-specific technical issues. Hreflang errors appear in Search Console’s International Targeting report. Check crawl stats to ensure Google is accessing all language versions. Monitor Core Web Vitals by country – site speed varies geographically.
Track conversion funnel drop-off by market. If German traffic converts at 2% but UK traffic at 0.5%, you have a localization problem, not a traffic problem. Dig into checkout abandonment data to find friction points – payment methods, shipping costs, unclear policies.
Measure content performance per language. Which blog posts drive traffic in each market? Do certain content types perform better in specific countries? Use this data to inform content prioritization. Our ecommerce SEO dashboard breaks down performance by page type and market, letting you spot optimization opportunities across your international presence.
Calculate ROI by market. Not all countries deliver equal returns. Factor in translation costs, shipping logistics, payment processing fees, and tax compliance overhead. A market generating high traffic but negative margin should be deprioritized.
Common red flags: high bounce rates (localization issue), low time-on-site (wrong search intent), abandoned carts (shipping/tax surprises), 404 errors (broken hreflang or canonical chains).
Common international SEO pitfalls
I’ve audited dozens of international WooCommerce stores. The same mistakes appear repeatedly.
Automatic IP-based redirects without language selection frustrate users traveling internationally and prevent search engines from crawling alternate versions. Always provide visible language/country switchers.
Identical content across markets with only currency changed gets recognized by Google as low-effort duplication. Provide unique value per market or use hreflang to consolidate ranking signals.
Missing or incorrect hreflang implementation is pervasive. Non-reciprocal links, wrong ISO codes, relative URLs, missing x-default – these errors cause Google to ignore your international setup entirely.
Indexing parameter-heavy filtered URLs in multiple languages exponentially multiplies the crawl budget waste problem. Implement strict indexing controls on faceted navigation. Reference our WooCommerce faceted navigation SEO guide for implementation.
Expanding to too many markets simultaneously stretches resources impossibly thin. You can’t properly localize six countries at once with a small team. Start with 2-3 markets, validate the playbook, then scale.
Neglecting mobile optimization internationally kills conversion in markets where mobile commerce dominates, particularly in Southeast Asia. If your WooCommerce store isn’t mobile-optimized, you’ll fail internationally before you start.
Ignoring local search engines costs visibility in specific markets. Google dominates in most markets but not everywhere. If you’re targeting Russia, optimize for Yandex. China requires Baidu. Czech Republic has Seznam. Diversify your international SEO strategy beyond Google alone.
TL;DR
International WooCommerce SEO requires coordinated execution across site architecture, technical SEO, content localization, and operations. Use subdirectories for most international expansions to consolidate authority while maintaining clear language separation. Implement hreflang tags precisely – bidirectional linking, absolute URLs, ISO-compliant codes, and x-default fallbacks are non-negotiable. Don’t translate content; rewrite it based on local keyword research and cultural context. Configure shipping zones, tax rules, and payment methods for each target market to eliminate checkout friction. Create market-specific supporting content that addresses local search intent rather than translating existing blog posts. Measure performance by country and language segment to identify optimization opportunities. Start with 2-3 high-ROI markets, validate your localization playbook, then scale systematically. ContentGecko automates multilingual content creation and catalog synchronization, letting small teams manage international SEO at enterprise scale without manual content maintenance overhead.
