WooCommerce migration without losing SEO
Platform migrations fail because merchants treat them as technical operations when they’re actually SEO retention projects. 68% of failed e-commerce migrations stem from improper redirect implementation, creating 404 errors that permanently destroy ranking equity you spent years building.
I’ve watched stores lose 30-50% of organic traffic post-migration because they focused on moving data instead of preserving search visibility. The solution isn’t complicated – it requires methodical planning before you touch a single URL.

Pre-migration SEO audit
Document everything Google currently indexes before you change anything. This baseline determines what you need to redirect.
Crawl your entire site with Screaming Frog and export the full URL inventory. You need every product page, category, tag archive, blog post, and CMS page that exists in search results. Filter for HTTP 200 responses only – these are the URLs currently passing ranking signals.
Extract your top 500 organic landing pages from Google Search Console. Sort by impressions over the last 12 months. These URLs drive your search visibility and cannot 404 after migration. Most merchants skip this step and wonder why traffic drops 40% when their highest-ranking pages break.
Map your current URL structure to the new platform. Create a spreadsheet with three columns: old URL, new URL, redirect type (almost always 301). Include URL parameters if your products use filters or variations – variable products require special redirect mapping as standard redirects often fail to account for variation parameters.
One objection I hear constantly: “We’re moving to WooCommerce from Shopify – the URL structures are completely different.” Exactly. That’s why you map before migration instead of discovering broken links in Search Console three weeks later.
Document your internal linking patterns. Export your sitemap and identify which category pages link to which products. These relationships must persist after migration to maintain crawl efficiency. Broken internal links increase by 300% on average after improper migration, wasting crawl budget on 404s instead of indexable pages.
Data transfer checklist
Migration tools handle bulk transfers but miss edge cases that destroy SEO. Verify these elements transfer completely.
Products need SKUs, titles, descriptions, prices, stock status, images with original filenames, categories, tags, attributes, variations, and custom fields. Test a sample product with multiple variations – if variation URLs don’t transfer correctly, you’ll 404 every /product/?attribute_color=blue link in search results.
Categories and taxonomies require names, slugs, hierarchy, descriptions, images, and meta data. Your category structure determines URL paths. If “Women’s Shoes” migrates as “womens-shoes-1” instead of “womens-shoes,” every product URL under that category breaks and you lose the ranking signals from thousands of internal links.
Blog content and pages must preserve post content, publish dates, authors, featured images, meta descriptions, and custom post types. Incorrect permalink structure during migration breaks internal links, wasting crawl budget and potentially causing 20-30% traffic drop.
Media library images must maintain original paths or you’ll create thousands of 404s. Proper image path redirection prevents 25% of common 404 errors related to missing product media. Google has already indexed your product images – breaking those URLs removes products from image search results.
Customer and order data isn’t directly SEO-related but critical for business continuity. You need order history, customer accounts, addresses, and purchase patterns to maintain transactional email flows and retargeting campaigns that support organic revenue.
SEO metadata and settings include robots.txt rules, XML sitemap settings, canonical tag configurations, redirect rules from previous migrations, and noindex/nofollow settings on filtered pages. Most migration plugins ignore these entirely.
Run test migrations on a staging environment. Sites using staging testing before migration reduce critical SEO errors by 70% compared to direct production migrations. Crawl the staging site and compare it against your pre-migration baseline. Every URL mismatch becomes a redirect requirement.
URL mapping and 301 redirects
This step preserves your link equity. 301 redirects must be implemented for all URL types – product pages, categories, blog posts, CMS pages – to preserve link equity. 302 redirects do not pass SEO value.
Build your redirect map from the pre-migration audit. Your spreadsheet should now have old URL → new URL mappings for every indexable page. Prioritize redirects based on Google Search Console impressions – high-volume pages need perfect redirects.
Implement redirects at the server level via .htaccess or Nginx configuration. Server-level redirects execute before WordPress loads, reducing response time and avoiding redirect chains. A redirect chain (old URL → temp URL → final URL) dilutes link equity with each hop.
Example .htaccess redirect for a category:
Redirect 301 /old-category/product-name https://yourstore.com/new-category/product-nameFor bulk redirects, use a plugin like Redirection that logs 404 errors and allows regex patterns. Our guide on WooCommerce redirects covers implementation details. But verify every redirect actually works – most merchants implement redirects, assume they work, then discover 404s weeks later when traffic has already dropped.
Test your redirects with HTTP status code checkers before going live. Use httpstatus.io or curl commands to verify each redirect returns a 301 response and lands on the correct final URL. Check redirects for standard product pages, products with variations and URL parameters, category and tag archives, paginated category pages (most merchants forget these), blog posts and informational pages, and old promotional landing pages.
Proper URL mapping before migration reduces post-migration traffic loss by up to 85% compared to sites without pre-migration planning.
Canonical tags and duplicate content
Migrations frequently create duplicate content issues when both old and new URLs temporarily exist. 73% of migration-related SEO issues stem from duplicate content problems.
Implement self-referencing canonical tags on every new URL immediately after migration. Your SEO plugin (Yoast, Rank Math, AIOSEO) should handle this automatically, but verify by checking page source. A product at /new-category/product-name needs:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourstore.com/new-category/product-name" />Canonicalize product variations to the parent product. If you sell a blue shirt and a red shirt as variations, both variation URLs should canonical to the main product page. This consolidates ranking signals instead of splitting them across duplicate content. Our WooCommerce canonical tags guide covers detailed implementation.
Set correct canonicals for filtered and sorted category pages. When customers filter by price or sort by popularity, your URL might change to /category/?filter=price-high-low. These filtered views should canonical to the main category page unless the filter creates genuinely unique content worth ranking separately.
Canonical tag errors cause 65% of duplicate content issues during platform migrations, requiring manual verification of all canonical URLs. Don’t assume your plugin gets this right – test product pages, categories, and blog posts individually. More troubleshooting guidance is available in our WooCommerce duplicate content article.
Structured data validation
Product schema drives rich results in search. Break it during migration and your CTR drops immediately.
Validate schema on your new site within 48 hours of migration. Sites that validate structured data within 48 hours maintain 98% of rich result impressions versus 60% drop for delayed validation. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to verify product, offer, and review schemas render correctly.
Verify these schema types transfer completely: Product schema (name, SKU, image, description), Offer schema (price, currency, availability, shipping), AggregateRating (average rating, review count), Review schemas for products with customer feedback, and BreadcrumbList for category hierarchy.
Test a standard product, a variable product, a sale product, and an out-of-stock product. Each scenario requires different schema values. If availability shows “InStock” for an out-of-stock product, Google may remove your rich results entirely for schema quality violations.
Structured data must be manually validated post-migration using Google’s Rich Results Test to maintain rich snippets. Most WooCommerce SEO plugins output schema automatically, but migration can break plugin settings or introduce conflicts. Our WooCommerce structured data guide covers comprehensive implementation.
Internal linking preservation
Search engines use internal links to understand site architecture and pass authority between pages. Broken internal links after migration waste crawl budget and isolate pages from ranking signals.
Audit internal links on your new site immediately. Screaming Frog’s “Links” report shows which pages link where. Filter for broken internal links – any link pointing to a URL that 404s or redirects. Fix these by updating the link to point directly to the final URL.
Update navigation menus, footer links, and sidebar widgets to use new URL structures. These template elements appear on every page and create thousands of links sitewide. If your category menu still points to old URLs, you’re internally linking to redirects instead of final destinations.
Verify product cross-links and related product recommendations use the new URL structure. If related products pull from old URL data, you’ll have correct redirects but inefficient internal linking that forces Google to follow redirects unnecessarily.
Regenerate your XML sitemap after migration and submit it to Google Search Console. Your sitemap tells Google which URLs to crawl. An outdated sitemap pointing to pre-migration URLs delays indexation of new pages. Our WooCommerce XML sitemap guide covers optimization best practices, and our breadcrumbs SEO guide explains how navigational structure affects crawling.
83% of recovered traffic depends on immediate submission of updated sitemaps to Google Search Console. This signals Google that your site structure changed and provides the new URL list for re-crawling.
Post-migration monitoring
Migrations always have edge cases. Monitor closely for 30 days to catch issues before they compound.
Track 404 errors in Google Search Console under Coverage reports. The “Not found (404)” section shows which URLs Google attempted to crawl but couldn’t find. These are either missing redirects or broken internal links. Post-migration SEO neglect allows small issues to compound, causing 50%+ longer recovery time for traffic.
Monitor organic traffic by page type in Google Analytics. Create segments for products, categories, and blog posts. If product traffic recovers but category traffic drops, you likely have category URL or internal linking issues specific to that page type. The ContentGecko SEO dashboard breaks down Search Console metrics by page type automatically, making it easier to spot segment-specific problems.
Watch rankings for your top 50 keywords. Use a rank tracker or Google Search Console’s Performance report filtered by query. Sites implementing comprehensive pre-migration SEO audits recover 95% of organic traffic within 30 days versus 90+ days for unprepared migrations. If rankings drop for high-volume queries, investigate the specific URLs that rank for those terms.
Check mobile performance and Core Web Vitals. Sites that neglect mobile performance audit during migration experience 40% higher bounce rates due to mobile-first indexing penalties. Your new platform may have different mobile optimization requirements.
How ContentGecko preserves SEO during migration
Migrations disrupt content ecosystems – blog posts that linked to old product URLs now point to redirects, internal linking patterns break, and supporting content becomes outdated.
ContentGecko maintains SEO equity during and after migration through catalog synchronization. When you connect ContentGecko to your new WooCommerce store via our WordPress connector plugin, the platform syncs product URLs automatically and updates internal links in published content. When /old-category/product-name becomes /new-category/product-name, ContentGecko rewrites links in existing blog posts to point to the new URL directly – no redirects needed for internal links.
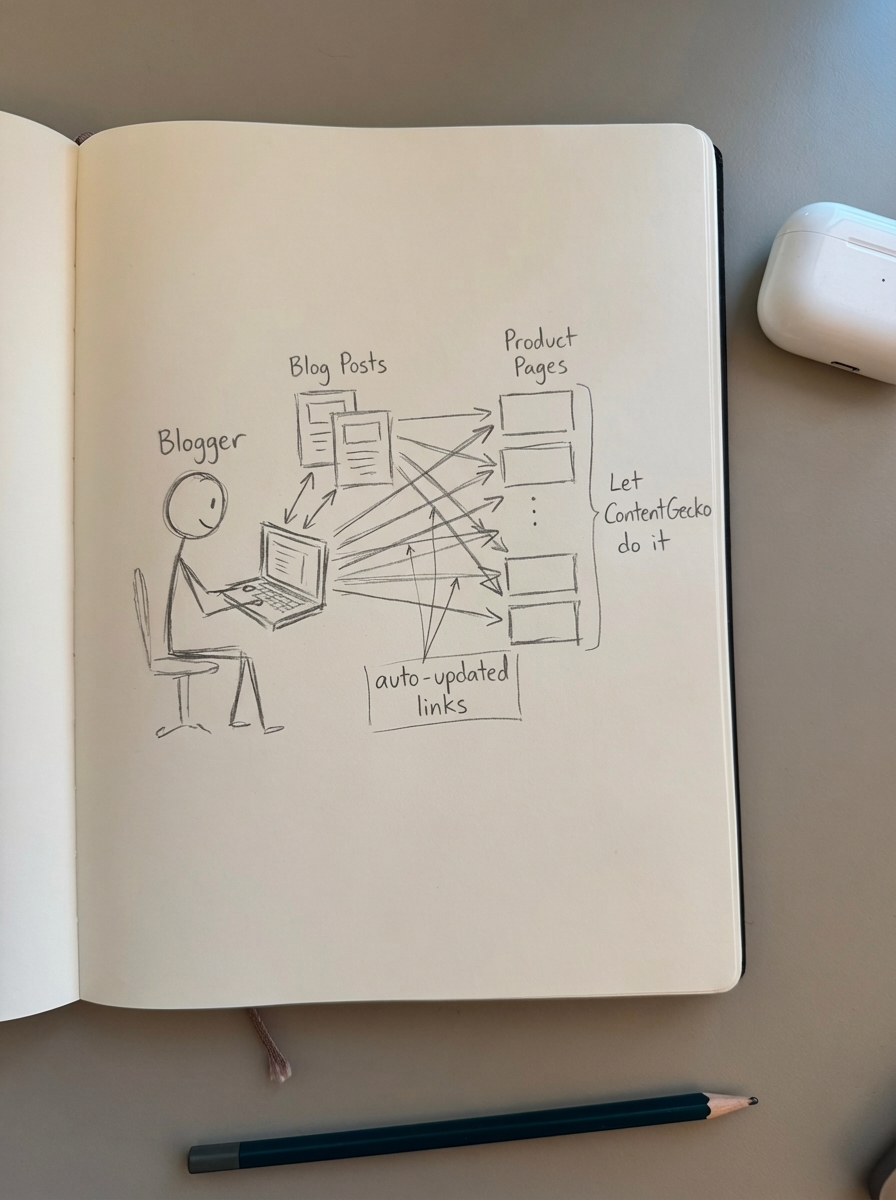
The platform regenerates schema markup for product mentions in blog content. If a product’s price, availability, or URL changes during migration, ContentGecko updates the structured data embedded in supporting content to maintain rich result eligibility.
ContentGecko creates URL mapping for SEO content to preserve blog post rankings. If your blog lives at /blog/ pre-migration and moves to /articles/ post-migration, ContentGecko handles the redirect implementation and updates internal cross-links between blog posts automatically.
The system monitors ranking changes post-migration and identifies content that needs updating. If a blog post about “best running shoes” drops in rankings after migration because the linked products changed URLs, ContentGecko flags the post for review and can regenerate sections that reference out-of-date product information.
This matters for stores with extensive content libraries. Manually updating hundreds of blog posts to reflect new product URLs and schema requirements takes weeks. AI-powered keyword processing handles 1,000 keywords in 3 minutes, letting you redirect resources to strategic migration planning instead of manual content updates.
For migration planning specifically, use our free keyword clustering tool to identify which keywords drive traffic to which page types. This helps prioritize redirect implementation – high-volume keyword clusters targeting specific URLs need perfect redirects, while low-traffic long-tail pages can be handled in batches.
Common migration mistakes that destroy SEO
Even with planning, merchants make predictable errors.
Redirecting all old URLs to the homepage is SEO suicide. Google interprets mass-homepage redirects as soft 404s and drops your rankings immediately. Every old URL needs a relevant destination – product to product, category to category, blog post to equivalent blog post.
Using 302 temporary redirects instead of 301 permanent redirects loses link equity. 302s don’t pass ranking signals. If you accidentally implement 302s site-wide, you lose all the ranking signals from backlinks and internal links. 301 implementation preserves 90-95% of referral traffic versus 40-60% loss with improper redirects.
Forgetting to redirect URL parameters creates hidden 404s. If your old site used /product/?color=blue for variations, you need redirects for those parameter-based URLs too. Redirecting only /product/ loses all the ranking signals from variation-specific backlinks.
Not redirecting category pagination loses long-tail rankings. Category/tag pagination URLs must be redirected to maintain long-tail keyword rankings that contribute 15-20% of organic traffic. Pages like /category/page/2/ have their own backlinks and rankings.
Changing URL structure unnecessarily creates work. If your old URLs included categories (/category/product-name/) and worked well, keep that structure on the new platform. The best migration preserves as many URLs as possible. Our WooCommerce URL structure guide covers optimization recommendations.
Skipping the staging environment means fixing mistakes in production after Google has already crawled broken links. Sites using staging testing reduce critical errors by 70%.
TL;DR
WooCommerce migrations preserve SEO through methodical pre-migration auditing, comprehensive 301 redirect implementation, canonical tag verification, structured data validation, and internal link updates. 68% of migrations fail due to improper redirects – success requires treating migration as an SEO retention project, not just a technical data transfer.
Build your redirect map before touching URLs, implement 301s at server level for every indexable page, verify canonical tags and schema immediately post-migration, and monitor 404 errors for 30 days. Sites with comprehensive pre-migration audits recover 95% of traffic within 30 days versus 90+ days for unprepared migrations.
ContentGecko automates post-migration content updates by syncing product URLs, regenerating schema, and maintaining internal link accuracy across blog content – critical for stores with large content libraries where manual updates would take weeks. Check our case studies to see how automated SEO content helps stores maintain and grow organic traffic during platform transitions.
