WooCommerce SEO checklist: The step-by-step guide for store owners
WooCommerce SEO isn’t rocket science, but it is systematic. Most stores leave easy wins on the table because they lack a clear process.
This checklist walks you through the must-do items for product page optimization, site architecture, technical SEO, and on-page work. Whether you’re running 50 SKUs or 50,000, you’ll find the exact steps to improve rankings and revenue.
Product page optimization
Product pages are your revenue drivers. They need to rank and convert.

Core on-page elements
Title tags: Include your primary keyword, a distinguishing feature, and your brand. Keep it under 60 characters. Example: “Organic Cotton Men’s T-Shirt – Lightweight | YourBrand”
Meta descriptions: Write 150–160 characters with a CTA. This is your SERP sales pitch.
H1 tags: Use your product name as the H1. Don’t overthink it.
Product descriptions: Write at least 300 words. Products with detailed descriptions perform significantly better in search. Include specifications, use cases, and benefits. Stop copying manufacturer content.
URLs: Keep them short and keyword-focused. /organic-cotton-mens-tshirt/ beats /shop/products/item-12345-blue/.
Image optimization
Name files descriptively before upload (mens-organic-cotton-tshirt-front.jpg, not IMG_0042.jpg). Compress images to under 200KB without visible quality loss. Write alt text for every image. Consider an image sitemap if you have a large catalog.
I’ve seen stores double their image search traffic just by fixing these basics.
Schema markup
Implement Product schema with name, SKU, image, price, and availability. Add AggregateRating schema when you have reviews.
Product schema markup increases conversions by 35%. Rich snippets can increase CTR by 35–45%. Most SEO plugins (Yoast, Rank Math) handle this automatically, but verify with Google’s Rich Results Test.
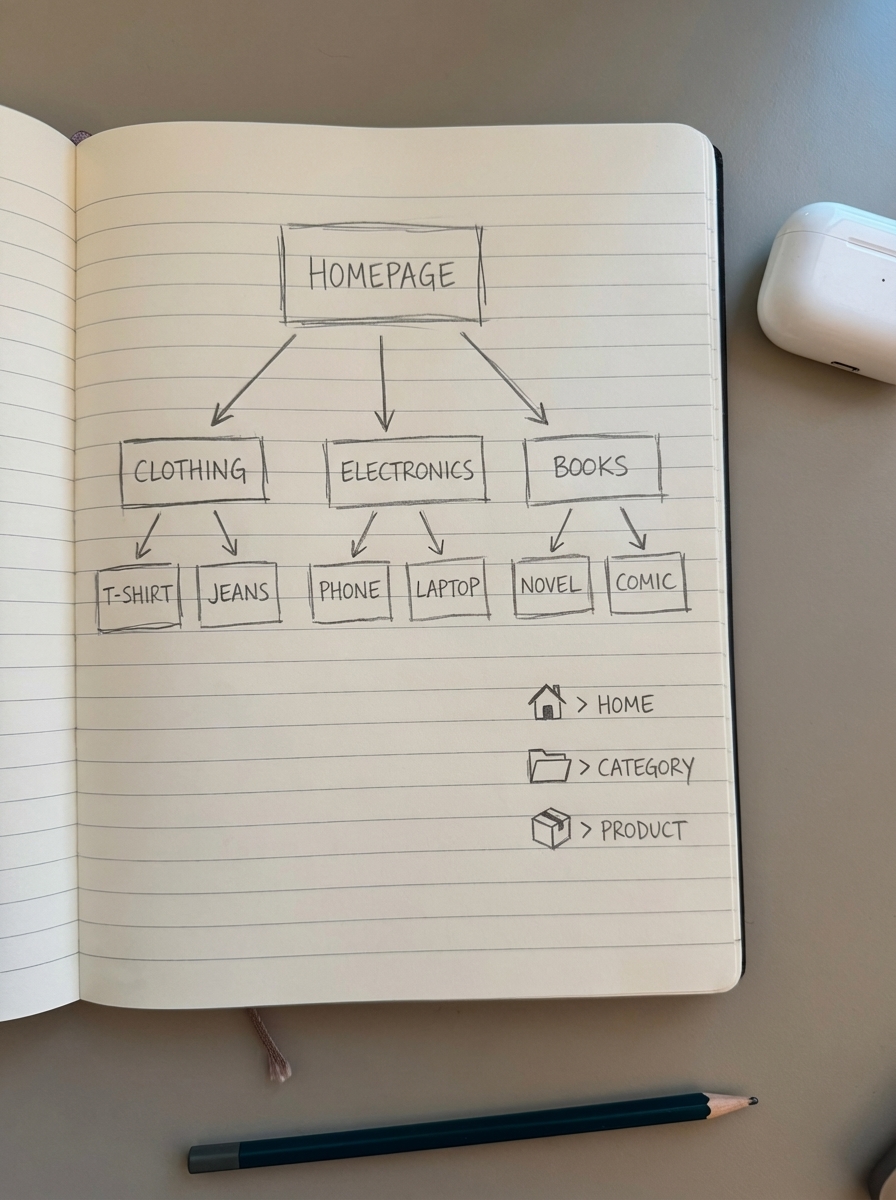
Site architecture and navigation
Google judges your store by how you organize it.
URL structure
Use “Post name” permalinks in Settings > Permalinks. Google explicitly prefers readable words over ID numbers in URLs.
Recommended structure: Include categories in product URLs (/category/product-name/). This creates logical hierarchy and reinforces topical relevance.
URL best practices: Keep URLs under 3 subdirectory levels. Use hyphens, not underscores. Include target keywords. Remove the /product-category/ base to shorten URLs.
Category and taxonomy organization
Build clear parent/child category relationships. Keep important products within 2–3 clicks of the homepage – products reachable within this range improve crawl efficiency and user flow. Write unique descriptions for category pages. Use ContentGecko’s free category optimizer to find better category names.
Most stores use vague category names. “Men’s Shirts” loses to “Organic Cotton Men’s Dress Shirts” every time.
Breadcrumb implementation
Enable breadcrumbs with proper schema markup. They help users navigate and show Google your site structure. Stores with good breadcrumbs often see a 5–15% improvement in organic CTR.
Configure through your theme or an SEO plugin. Verify the BreadcrumbList schema appears in your source code.
Internal linking
Link related products on each page. Link from blog posts to relevant category and product pages. Use descriptive anchor text that naturally fits the sentence.
Internal linking spreads link equity and keeps crawlers moving through your catalog. It also increases time on site and average order value.
Technical SEO fundamentals
This is where most stores break without knowing it.
Core Web Vitals
Google’s thresholds: LCP ≤2.5s, FID ≤100ms, CLS ≤0.1. Sites loading under 2 seconds have 42% lower bounce rates.
Quick fixes: Use performance-focused hosting (avoid $5/month shared hosting). Enable a CDN. Install WP Rocket or similar caching plugin. Lazy load images. Minify CSS/JS.
Test your store with Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse.
HTTPS and security
HTTPS is mandatory and a ranking factor. Sites without SSL lose trust signals and rankings immediately. Google uses HTTPS as both a ranking factor and trust signal for checkout security.
Ensure your entire site uses HTTPS. Check for mixed content warnings and update all internal links.
Mobile optimization
Google uses mobile-first indexing. Non-mobile-friendly sites lose visibility. Test your store on real devices. Check that buttons are tappable, text is readable without zooming, and checkout works smoothly.
XML sitemap
Your sitemap tells search engines what to crawl. WordPress generates basic sitemaps, but for WooCommerce you need more.
What to include: All product pages, category pages, and important blog posts.
What to exclude: Cart, checkout, account pages, low-value filter combinations, and attachment pages.
Use Yoast, Rank Math, or XML Sitemap Generator for Google. Submit your sitemap in Google Search Console.
Robots.txt configuration
Your robots.txt file controls crawler access. Always block /cart/, /checkout/, and /my-account/. Include your sitemap URL. Never block product pages, category pages, images (/wp-content/uploads/), or AJAX functionality.
Test in Google Search Console robots.txt Tester. A SEMrush study found 72% of e-commerce sites block indexable content by mistake.
Canonical tags
Proper canonicals prevent duplicate content issues. WooCommerce creates duplicates from product variations, filter URLs, and pagination. Proper canonicalization prevents 63% of duplicate content issues in WooCommerce implementations.
Rules: Product variations should canonicalize to the parent product. Filtered category pages should canonical to the main category. Paginated pages should self-reference.
Configure through Yoast or Rank Math. Use ContentGecko’s keyword clustering tool to spot cannibalization issues where multiple pages compete for the same keywords.
Faceted navigation
Filters can generate thousands of useless URLs. Stores can waste 70% of crawl budget on low-value filter combinations. Using rel="nofollow" on non-primary filter combinations prevents crawl budget waste.
Strategy: Index only high-demand filter combinations. Noindex other filter pages. Use rel=“nofollow” on low-value filter links. Block parameter-heavy URLs in robots.txt.
Find which filters have search demand using keyword research. Index those. Block the rest.
On-page SEO tactics
Beyond product pages, these elements improve site-wide SEO.
Keyword strategy
Stop guessing at keywords. Use tools (Ahrefs, SEMrush, ContentGecko’s clustering tool) to find what people actually search.
Focus on: Primary product keywords (what it is), long-tail modifiers (specific features), product-specific terms (model numbers, specs), and question-based keywords for blog content.
E-commerce retailers using intent-based clustering for product descriptions saw 43% increase in organic traffic and 27% rise in qualified leads.
Content creation
Blog posts targeting how-tos, buying guides, and comparison articles drive traffic to product pages. Write for search intent. If someone searches “best running shoes for flat feet,” give them that comparison, not a generic brand story.
ContentGecko’s AI content writer can generate catalog-aware articles that automatically link to your products and update when your inventory changes.
Review management
Customer reviews improve conversion rates and provide fresh content for search engines. Encourage reviews post-purchase. Respond quickly – responding within 24 hours increases trust scores by 28%.
Implement review schema markup to show star ratings in SERPs.
Automation and maintenance
SEO isn’t one-and-done. Products change. Prices update. URLs shift.
Manual maintenance doesn’t scale past a few hundred products. This is where automation becomes critical.
ContentGecko syncs with your WooCommerce catalog to automatically update SEO elements when products change. It handles schema markup, internal linking, content updates, and performance monitoring without manual work.
Weekly tasks: Check for broken links and images. Monitor Google Search Console for errors. Review top-performing pages.
Monthly tasks: Audit product page performance. Update product descriptions for seasonal changes. Review keyword rankings.
Quarterly tasks: Full technical SEO audit. Competitive analysis. Content gap identification.
For large catalogs (1,000+ products), automation isn’t optional. AI-powered automation can process 1,000 WooCommerce keywords in 3 minutes, freeing you to focus on strategy instead of busywork.
Measuring success
Track these metrics to know what’s working.
Google Search Console: Impressions and clicks by page type, coverage issues, and Core Web Vitals status.
Analytics: Organic traffic to product/category pages, assisted conversions from blog content, and revenue per traffic source.
Technical health: Crawl budget efficiency, index coverage rate, and page speed scores.
Use ContentGecko’s ecommerce SEO dashboard to see performance broken down by product pages, categories, and blog posts separately.
TL;DR
WooCommerce SEO comes down to execution on five areas:
- Product pages: Optimize titles, descriptions, images, and schema. Write unique content over 300 words per product.
- Site architecture: Use category-based URLs, implement breadcrumbs, keep products within 3 clicks of homepage.
- Technical SEO: Fix Core Web Vitals, configure robots.txt and sitemaps, handle canonicals and faceted navigation properly.
- On-page content: Target intent-based keywords, create helpful blog content, collect and markup reviews.
- Automation: Use tools like ContentGecko to keep SEO elements updated as your catalog changes.
Start with the highest-traffic products and categories first. Fix technical issues site-wide. Then expand optimization across your catalog. For stores with 1,000+ products, automation becomes essential to maintain SEO at scale.
