WooCommerce SEO plugin setup: Configuration guide for Yoast and Rank Math
SEO plugins handle the repetitive technical work that keeps your WooCommerce store visible in search. I’ve configured hundreds of stores, and the setup process determines whether you spend months fixing indexation issues or see traffic gains within weeks.
Rank Math offers built-in WooCommerce SEO features in its free version, while Yoast requires a separate $178.80/year add-on for the same functionality. Both work, but your choice affects long-term costs and the features available out of the box.
Choosing between Rank Math and Yoast for WooCommerce
Rank Math’s free version includes WooCommerce schema markup, product optimization, redirect management, and 404 monitoring. Yoast locks most of these behind premium tiers. Rank Math Pro starts at $6.99/month for unlimited sites versus Yoast’s $118.80/year per site.

The feature gap matters for stores with 1,000+ products. Rank Math includes automatic image alt attributes and semantic keyword suggestions in the free version. Yoast Premium doesn’t offer semantic analysis even at premium pricing. For agencies managing multiple stores, Rank Math’s pricing model saves thousands annually.
Performance is another consideration. I’ve seen Yoast add 200-300ms to page load times on some configurations, while Rank Math’s modular system lets you disable unused features to reduce bloat. Since every 100ms improvement correlates with 1.3% higher conversion rates, this adds up.
Rank Math also integrates Google Search Console and Analytics without requiring premium upgrades. Yoast gates this behind the paywall.
For most WooCommerce stores, Rank Math offers better value. Use Yoast if you’re already invested in their ecosystem or prefer their specific interface – just budget for the WooCommerce add-on.
Installing and activating your chosen plugin
Never run Yoast and Rank Math simultaneously. Using multiple SEO plugins creates rule conflicts as they overwrite each other’s canonical tags, meta descriptions, and schema markup.
If migrating from Yoast to Rank Math, install Rank Math via Plugins → Add New, then run the Setup Wizard and select “Import from Yoast SEO.” Rank Math imports all SEO data including redirects without affecting rankings. Verify import completion in Rank Math → Status & Tools → Import & Export, then deactivate and delete Yoast only after confirming data transfer.
For fresh installations, install your chosen plugin and follow the setup wizard. The wizard configures 80% of what you need – don’t skip it trying to save time.

Rank Math setup wizard walkthrough
The wizard asks about your site type, company info, and Search Console connection. Here’s what matters for WooCommerce.
Choose “Organization” for site representation and enter your business name, logo URL, and contact details. This populates Organization schema across your site.
Connect your GSC account when prompted. This enables keyword tracking and indexation monitoring directly in WordPress.
Enable products and categories in sitemap settings, but disable tags unless you actively optimize them. Rank Math will create product and category sitemaps automatically.
Enable WooCommerce SEO, Schema, Redirections, and 404 Monitor under module selection. Disable modules you won’t use – Local SEO, News SEO – to reduce overhead.
The wizard auto-configures robots.txt rules to block cart, checkout, and account pages while allowing product pages. Verify at yoursite.com/robots.txt after setup.
Yoast setup wizard walkthrough
Yoast’s wizard covers similar ground with different terminology.
Choose “Production” for live stores or “Staging” for dev sites under environment settings.
Select “Online store (WooCommerce)” for site type to enable product-specific features.
Input company name, logo, and social profiles under organization details for Knowledge Graph optimization.
Let Yoast crawl your store during site analysis. The analysis identifies common issues like missing alt text or thin product descriptions.
If you purchased the WooCommerce SEO add-on, activate it via Yoast SEO → Extensions. The add-on is required for product schema, brand taxonomy, and structured data management.
Yoast creates sitemaps automatically but doesn’t include product variations by default. Enable variations under Yoast SEO → Search Appearance → Products → “Show product variants in sitemap.”
Product page optimization settings
This is where store-specific SEO happens. Both plugins let you set global defaults and override individual products.
In Rank Math, go to Rank Math → Titles & Meta → Products and configure your title template as %title% | %sitename% or %title% - %category% | %sitename% if you want category context. Set meta description template to %wc_shortdesc% to pull your WooCommerce short description automatically. Enable “Product” schema under Add Schema Markup (on by default). Set product condition default to “NewCondition” unless you sell used items. Enable brand taxonomy under Rank Math → WooCommerce SEO and map it to your custom brand attribute.
In Yoast with WooCommerce SEO add-on, navigate to Yoast SEO → Search Appearance → Products. Set SEO title to %%title%% %%sep%% %%sitename%% and meta description to %%wc_shortdesc%% or write a custom template. Yoast adds Product schema automatically if the add-on is active. Enable brand taxonomy under WooCommerce → Settings → Products to create a custom brand field.
For individual products, scroll to the SEO meta box below the product editor. Override titles, descriptions, and focus keywords as needed. I prioritize high-margin products first – optimize your top 20% revenue generators before touching long-tail SKUs.
The ContentGecko WordPress connector plugin automates much of this for large catalogs, maintaining optimized product pages and updating schema when prices or stock levels change.
Category page optimization settings
Category pages drive most transactional traffic in my experience. Searchers looking for “men’s running shoes” land on category pages, not individual products.
For Rank Math category settings, go to Rank Math → Titles & Meta → Product Categories. Set title to %term% %sep% %sitename% or Shop %term% %sep% %sitename%. Use %term_description% for description to pull the WooCommerce category description. Enable breadcrumbs under Rank Math → General Settings → Breadcrumbs to display proper URL structure navigation.
For Yoast category settings, navigate to Yoast SEO → Search Appearance → Taxonomies → Product categories. Set SEO title to %%term_title%% %%sep%% %%sitename%% and meta description to %%term_description%%.
Write unique 150+ word descriptions for your main categories. I’ve seen category pages with rich descriptions outrank product pages for commercial keywords because Google views them as comprehensive resources.
Use the free category optimizer to identify category naming opportunities – most stores use vague category names that don’t match search intent.
Schema markup and rich results configuration
Proper product schema increases rich result CTR by 30% versus standard blue links. Both plugins handle basic Product schema, but verification is critical.
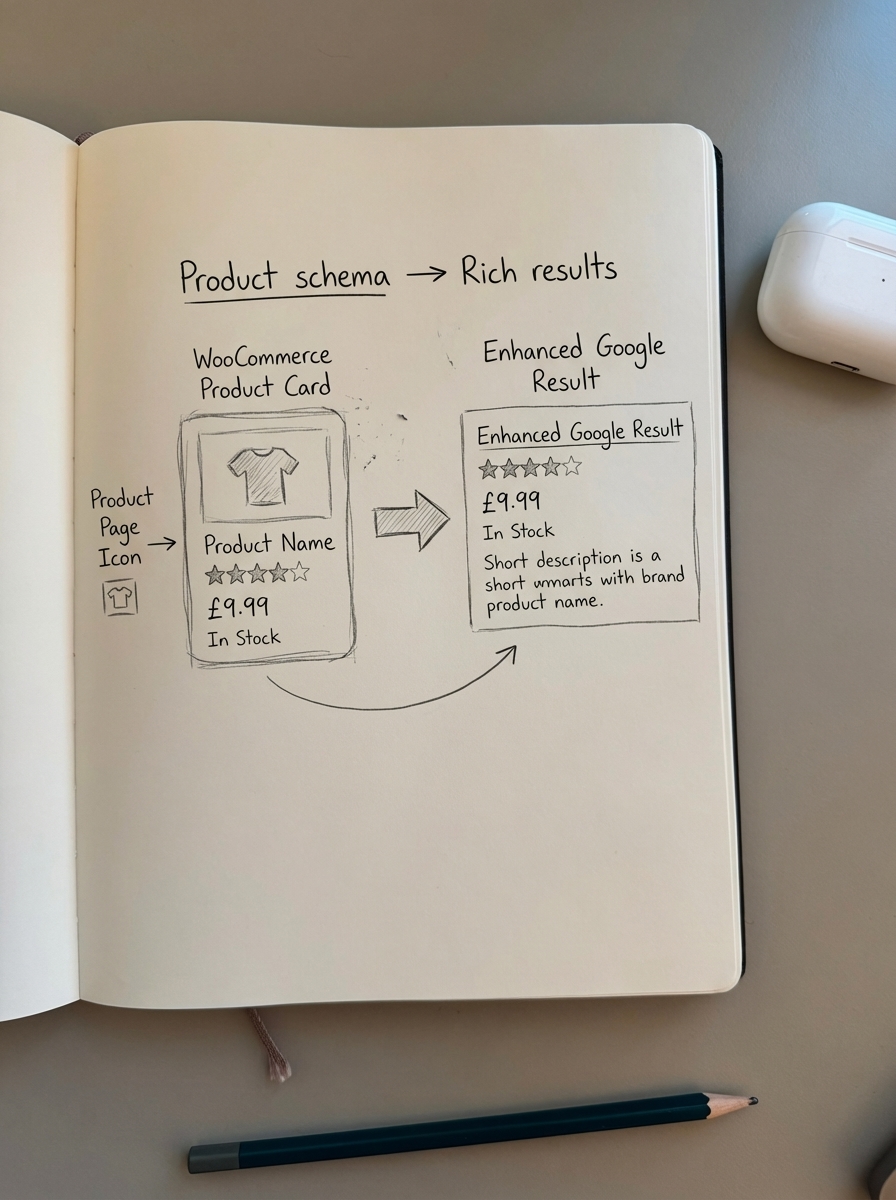
Rank Math generates Product schema automatically for WooCommerce products under Rank Math → Schema. It includes product name, image, description, price, currency, availability, AggregateRating (if reviews exist), and brand (if taxonomy is configured). Add FAQ schema manually to product pages using Rank Math’s schema generator for common questions. For example, on a tent product page, add FAQs about waterproofing, capacity, or setup time.
Yoast WooCommerce SEO adds Product schema when the add-on is active. It’s less flexible than Rank Math – you can’t add supplementary schema types without custom code.
Test every schema implementation by opening Google Rich Results Test, entering a product URL, verifying “Product” appears as a detected structured data type, and checking for errors like missing offers, invalid availability, or missing image URLs.
Common schema errors I see include missing offers when products are set to “Catalog Visibility: Hidden,” invalid aggregateRating when no reviews exist, and missing required image URLs in schema markup.
Monitor Rich Results in Google Search Console under Enhancements → Product. Fix errors before they compound across your catalog.
Technical SEO settings: Sitemaps, robots.txt, canonical tags
The plugin handles most technical SEO, but you need to verify configurations for WooCommerce-specific edge cases.
Both plugins auto-generate XML sitemaps at /sitemap.xml or /sitemap_index.xml. Enable products and categories, disable product tags (unless you optimize tags), disable product variations (causes duplicate content), and include out-of-stock products if you restock regularly.
Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console immediately after setup. Go to Sitemaps → Add new sitemap → enter sitemap.xml.
Configure robots.txt to block low-value pages. In Rank Math, go to Rank Math → General Settings → Edit robots.txt. In Yoast, navigate to Yoast SEO → Tools → File Editor → robots.txt. Add directives to block cart, checkout, my-account, and parameterized URLs while allowing product images and the sitemap. This preserves crawl budget by blocking cart, checkout, and parameterized URLs while allowing product images and the sitemap.
Canonical tag configuration prevents duplicate content from product variations and filtered navigation. Both plugins add self-referencing canonicals by default. Override individual canonicals in the product/category editor if needed – for example, pointing filtered category pages back to the main category URL. Verify canonicals with: curl -A "Googlebot" https://yoursite.com/product-name/ | grep canonical. The tag should point to the canonical version of the page, not a parameter-heavy filtered URL.
Image optimization and alt text automation
Images represent 61.3% of page download time, and missing alt text reduces accessibility compliance by 68% while correlating with 15% lower image search CTR.
Rank Math generates alt text automatically when you insert images. It pulls from image filename (if descriptive), product title (for product gallery images), or manual alt field (if populated). Enable this under Rank Math → General Settings → Images → Auto add alt attributes.
Yoast Premium includes bulk alt text editing via CSV export. Navigate to Yoast SEO → Tools → Import and Export → Export to create a spreadsheet of all images, then re-import after editing. This works for smaller catalogs but becomes unmanageable above 1,000 products. I’ve seen teams spend 11 hours/week maintaining alt text manually.
For catalogs with hundreds or thousands of products, automation prevents alt text from becoming stale when you add new images or rename products. ContentGecko auto-generates keyword-rich alt text synced to product names and updates it when catalog data changes – case studies show 22% average organic image traffic growth in six months.
Compress images before uploading. Use ShortPixel or Imagify to convert JPEGs to WebP format, which reduces file sizes by 25-35% without visible quality loss.
Search Console integration and performance monitoring
Connecting Google Search Console lets you track indexation, coverage errors, and Core Web Vitals directly in WordPress.
For Rank Math integration, go to Rank Math → General Settings → Google Search Console, click “Get Authorization Code,” log in with your Google account, copy the authorization code and paste it into Rank Math, then select your property from the dropdown. Rank Math displays Search Console data (impressions, clicks, CTR, position) on the WordPress dashboard and in each post/product editor.
Yoast Premium includes limited Search Console integration via Yoast SEO → General → Webmaster Tools → Google Search Console. It doesn’t provide the dashboard-level insights Rank Math offers.
Even with plugin integration, check Search Console weekly for coverage errors (submitted URL not indexed, crawl errors), mobile usability issues, and Core Web Vitals failures (LCP >2.5s, CLS >0.1). Core Web Vitals improvements correlate with up to 20% higher conversion rates. Fix LCP issues by optimizing images, CLS issues by setting explicit dimensions on images and ads, and INP issues by reducing JavaScript execution time.
Use the ecommerce SEO dashboard to track performance by page type – category pages, product pages, and blog posts each require different optimization approaches.
Common mistakes and troubleshooting
Running WooCommerce’s built-in schema plus a plugin creates duplicate Product markup. Disable WooCommerce’s default schema by adding this to functions.php: remove_action( 'woocommerce_single_product_summary', 'woocommerce_template_single_meta', 40 ); or use a plugin-specific filter to disable WooCommerce schema in favor of your SEO plugin’s implementation.
I’ve debugged stores where 40% of products weren’t indexed because someone toggled “noindex” in bulk. Check Rank Math → Titles & Meta → Products → “Robots Meta” or Yoast SEO → Search Appearance → Products → “Show Products in search results.” Also verify WooCommerce → Settings → Products → “Catalog visibility” is set to “Shop and search results” for active products.
Faceted navigation creates duplicate content. If you filter products by color or price, the filtered URL should canonical back to the main category page. Both plugins handle this automatically, but verify with: curl -I https://yourstore.com/category/?color=blue | grep canonical. The canonical tag should point to the main category URL, not the filtered URL.
Caching plugins (WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache) sometimes cache old schema markup after plugin changes. Clear cache after any SEO plugin configuration change. Security plugins occasionally block SEO plugin API requests to Google. Whitelist your SEO plugin’s domain in your security plugin settings if Search Console integration fails.
Changing product base URLs (e.g., from /shop/product/ to /products/) breaks existing links. Always implement 301 redirects. In Rank Math, go to Rank Math → Redirections → Add New. In Yoast, use a separate redirect plugin like Redirection. Enter old URL and new URL, select “301 Moved Permanently,” and save. Monitor 404 errors in Rank Math → 404 Monitor or via Search Console.
Advanced optimization and scaling
Title/description A/B testing improves CTR by 5.7% on average when optimized for position-specific expectations. Test variations of price mentions in titles (“$29.99” vs. no price), urgency language (“Limited Stock” vs. standard description), and benefit-focused vs. feature-focused descriptions. Run tests for 30 days minimum to account for ranking volatility. Track CTR changes in Search Console segmented by query.
Use the free SERP keyword clustering tool to identify which keywords share search intent. This prevents cannibalization – targeting “blue running shoes” and “blue athletic shoes” on separate pages splits ranking signals because Google returns similar results for both. Cluster related keywords and target each cluster with a single page. For 200+ keywords, upgrade to the premium clustering tool.
Manual optimization fails above 1,000 products. You can’t maintain unique titles, descriptions, alt text, and schema for thousands of SKUs without automation. ContentGecko syncs directly to your WooCommerce catalog via the WordPress connector plugin and automatically generates SEO-optimized product descriptions, updates schema when prices or stock levels change, maintains proper canonical tags across product variations, and creates supporting blog content that links to products.
The AI content writer handles informational queries (“how to choose running shoes”) that support transactional pages. This approach captures searchers earlier in the buyer journey. Stores using automated content see reduced manual SEO work and improved organic visibility because updates happen continuously instead of quarterly.
TL;DR
Install Rank Math for better out-of-the-box WooCommerce features and lower costs, or Yoast if you need their specific ecosystem. Run the setup wizard to configure sitemaps, schema, and Search Console integration. Optimize product and category templates with keyword-rich titles and descriptions. Verify schema implementation via Rich Results Test. Configure robots.txt to block cart/checkout pages while allowing products. Enable automatic alt text generation and compress images to WebP. Monitor Search Console for coverage errors and Core Web Vitals issues. For stores with 1,000+ products, automation via ContentGecko eliminates manual maintenance and keeps SEO elements synchronized with your catalog.
