Aligning UX and SEO for WooCommerce performance
User experience and search engine optimization are functionally the same pursuit: providing the most relevant, performant answer to a user’s intent. Google’s algorithms increasingly rely on technical performance and engagement signals to determine rankings. If your WooCommerce store is difficult to navigate, slow to load on mobile, or buried under a confusing site architecture, your rankings will suffer regardless of how many keywords you integrate into your product descriptions.
Prioritize category pages over product pages
I often see merchants obsessing over individual product page SEO while leaving their category pages as bare-bones grids. This is a mistake. Category pages are your highest-leverage assets because they rank for broad, high-volume terms and provide the “thematic glue” for your store. In many cases, a well-optimized category page functions as a conversion-focused landing page. It requires unique introductory content – ideally between 150 and 250 words – alongside strategic internal linking and clearly defined unique selling points (USPs).
We have found that most ecommerce sites would benefit greatly from more specific category naming conventions. For instance, using “Men’s Waterproof Trail Running Shoes” is far more effective for both bots and buyers than a generic “Shoes” label. You can use our free ecommerce category optimizer to identify specific naming patterns that align with actual buyer search intent and improve your store’s discoverability.
![]()
Simplify site architecture and the three-click rule
Your information architecture (IA) should follow a logical hierarchy that allows both users and search crawlers to find any product within three clicks of the homepage. Think of your site structure as a city’s road system; a bloated structure with orphaned pages or deep-nested subcategories creates dead ends that waste Google’s crawl budget. To resolve this, I recommend flattening your hierarchy and adopting a logical domain.com/category/subcategory/product pattern.
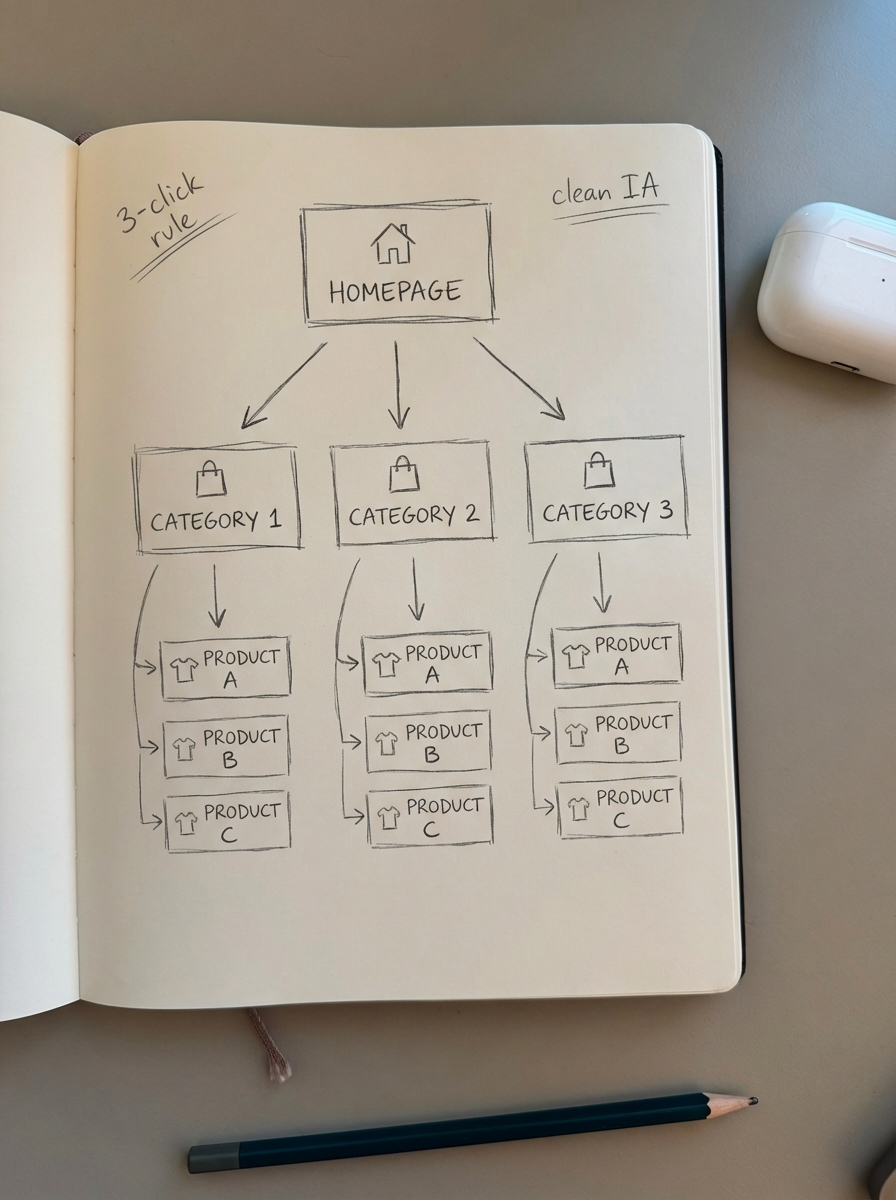
Authority distribution is equally critical, as link equity flows through your site like water in a pipeline. You can optimize this flow by using internal linking strategies that connect related categories and feature products directly within your category descriptions. Ensuring your WooCommerce URL structure remains clean and keyword-rich helps consolidate these signals. For a comprehensive look at organizing your store for scale, review our guide on SEO site structure essentials.
Optimize for Core Web Vitals and mobile-first indexing
Page speed is not merely a technical checkbox; it is a direct conversion lever. Research indicates that WooCommerce pages loading in under 3 seconds see bounce rates 40% lower than those taking 5 seconds or more. We focus on the “big three” Core Web Vitals for WooCommerce to maintain healthy rankings and user retention:
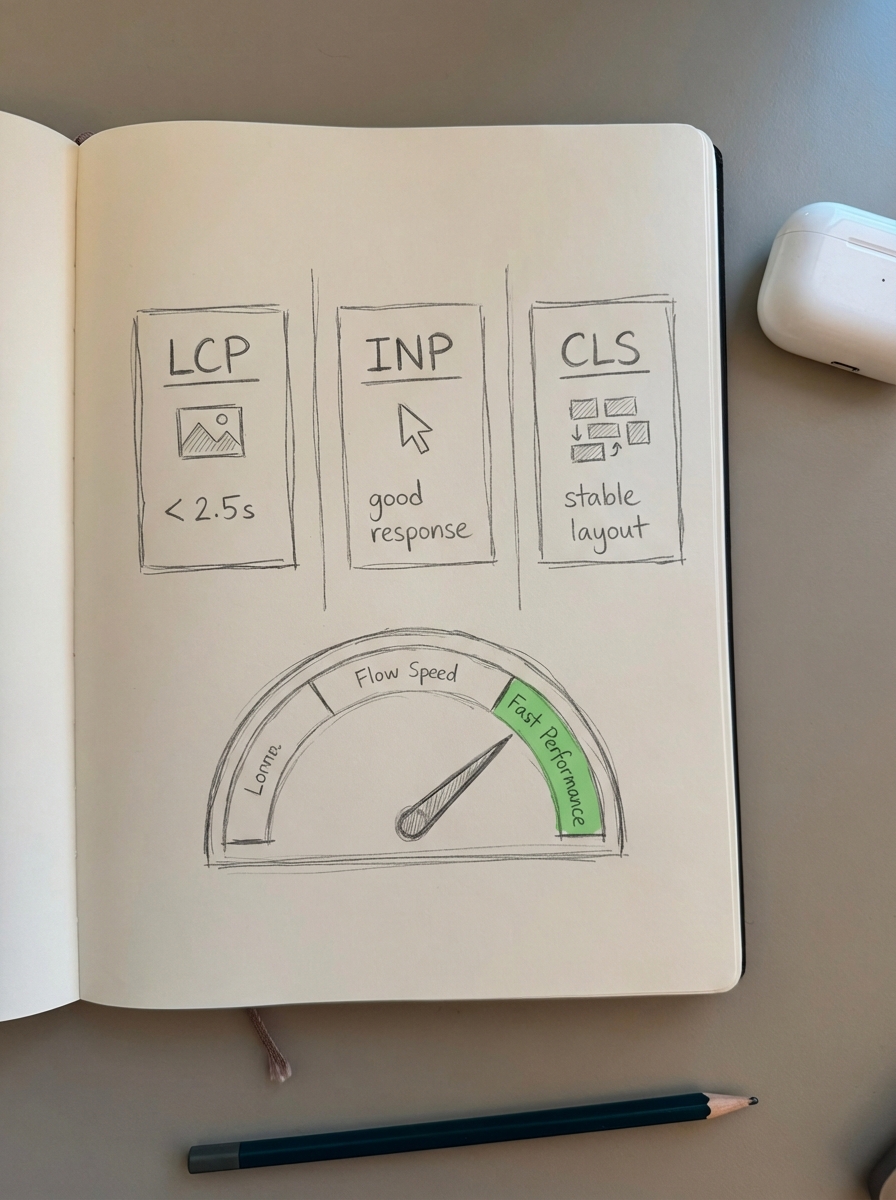

- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): You should aim for a score of 2.5 seconds or less. LCP is most frequently delayed by unoptimized product images that lack proper compression.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Target a score of 200ms or less. High INP is often the result of heavy third-party scripts or bloated AJAX cart fragments that delay user interactions.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Keep this score below 0.1 by reserving space for dynamic content like promotional banners, which prevents the page from “jumping” during the load process.
To hit these targets, I recommend moving to modern image formats like WebP or AVIF and leveraging a CDN to reduce your Time to First Byte (TTFB).
Implement smart navigation and search
Navigation must help users discover products without creating “index bloat,” which is a common challenge with faceted navigation SEO. If every combination of size, color, and price creates a unique, indexable URL, you will eventually face significant duplicate content issues. We use a tiered approach to manage this: index only high-value filter combinations that have documented search volume, while using noindex tags or robots.txt directives to block low-value combinations.
Integrating WooCommerce breadcrumbs with proper schema markup further aids search engines in understanding your hierarchy. This implementation can improve your organic click-through rate in the search results by up to 15%. I also suggest monitoring your internal site search data to find “failed searches.” If users are repeatedly searching for terms that do not have a corresponding category, that is your signal to create a new, optimized landing page for that intent.
Use a blog to bridge the gap between discovery and sales
If you have already optimized your technical foundations and category architecture, the remaining growth opportunity lies in content. Most buyers are not ready to purchase the moment they land on your site; they are often searching for how-to guides, listicles, or product comparisons. A catalog-aware blog allows you to capture this top-of-funnel traffic and drive it toward your revenue pages.
This is where ContentGecko simplifies the process. Our platform integrates directly through a WordPress connector plugin to plan and publish content that remains synced with your inventory. If a product’s price or stock status changes, your blog posts reflect that automatically. This creates a seamless user experience where readers are never directed to broken links or out-of-stock items, maintaining both UX integrity and SEO authority.
Measure what matters
Effective optimization requires moving beyond general ranking data. We use an ecommerce SEO dashboard to segment performance by page type. This allows you to see whether your traffic is originating from high-intent category pages or informational guides, which informs where your UX needs the most attention.
If your category pages are generating high impressions but few clicks, you likely have a WooCommerce CTR optimization problem caused by generic meta titles or a lack of structured data. Conversely, if users land on your product pages but bounce immediately, you should investigate your LCP performance or mobile layout friction. By treating UX and SEO as a single optimization workflow, you ensure that every rank increase translates directly into a conversion lift.
TL;DR
- Optimize category pages as your primary landing assets rather than focusing solely on individual products.
- Keep your site hierarchy shallow to ensure no product is more than three clicks from the homepage.
- Improve page performance to hit Core Web Vitals targets, specifically aiming for an LCP under 2.5 seconds.
- Control faceted navigation with canonicals and noindex tags to protect your crawl budget from index bloat.
- Deploy automated, catalog-synced content with ContentGecko to drive long-tail traffic and maintain internal link health.
