Entity-based keyword research strategies
Traditional keyword research is no longer sufficient because search engines have transitioned from matching strings of text to mapping relationships between concepts. To maintain visibility in a search landscape dominated by AI Overviews and Large Language Models (LLMs), you must pivot your strategy from “keyword optimization” to “entity optimization.”
What entities are and why they have replaced keywords
An entity is a unique, well-defined, and distinguishable thing or concept. In ecommerce, your brand is an entity, your specific SKUs are entities, and the specific pain points your customers experience are entities. Unlike a keyword, which is merely a sequence of characters, an entity acts as a node in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
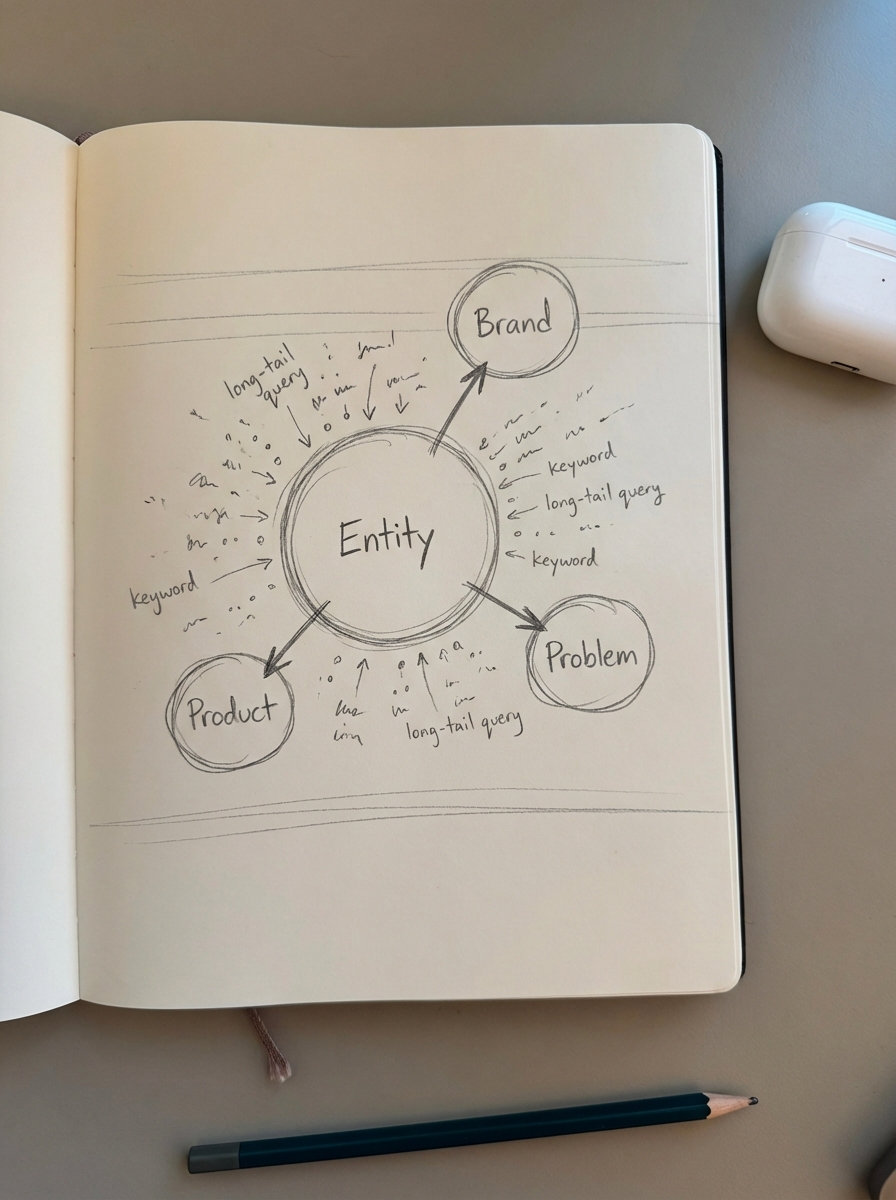
Modern search engines utilize Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the context behind a user’s query. For example, if a consumer searches for “best shoes for standing all day,” Google does not simply hunt for that exact phrase. It identifies relevant entities such as specific brands known for support, attribute entities like arch cushioning, and relationship entities like nursing or retail work.
I have observed that focusing on entities allows you to capture traffic from a massive range of long-tail queries that you may not have explicitly targeted in your copy. Research suggests that entity-focused content can rank 2-3 positions higher for these specific queries because search engines recognize the topical authority established through clear relationship mapping.
The strategic shift: From strings to things
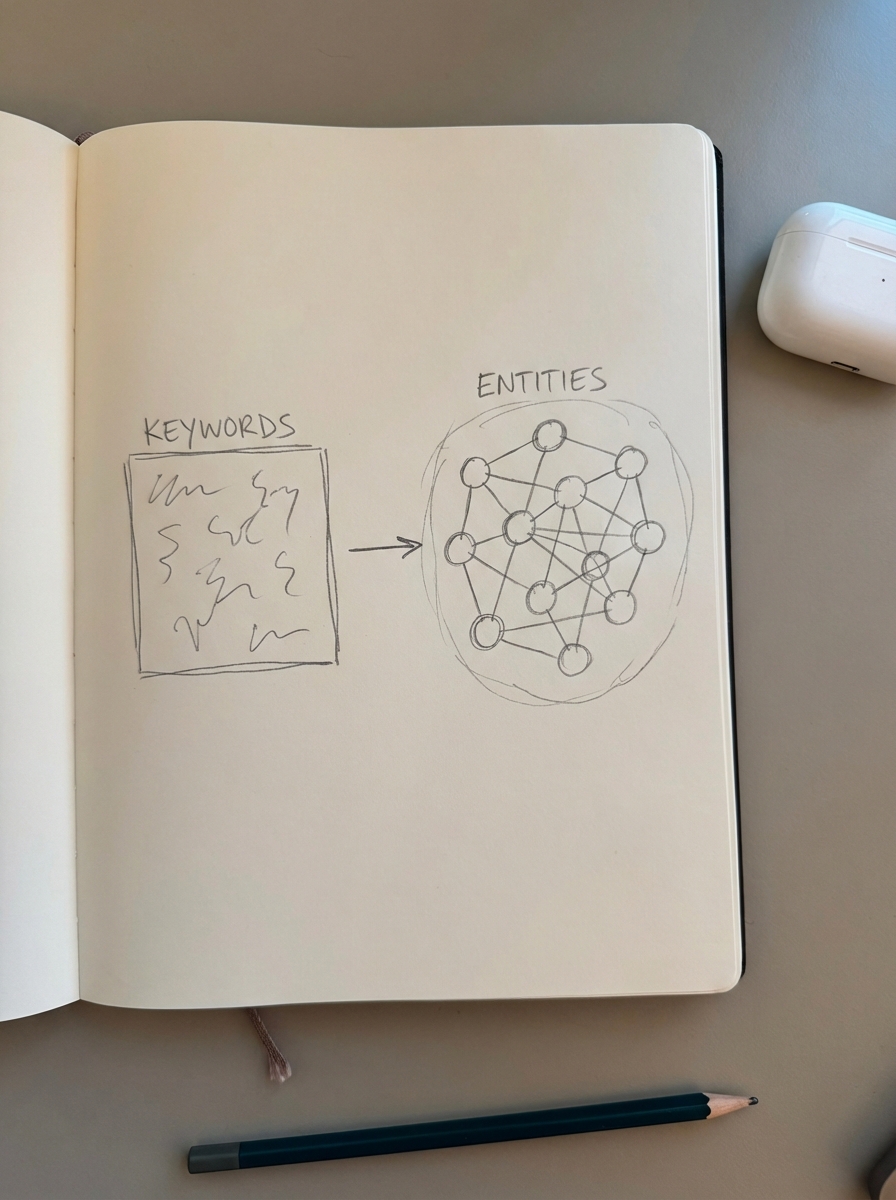
The fundamental flaw in traditional keyword research is its reliance on third-party volume data. At ContentGecko, we find that most third-party keyword data is inaccurate because the databases are too small and the search volume metrics are often lagging. Chasing high-volume keywords often leads to a “me-too” content strategy that fails to establish real authority.
We prefer to focus on entity clarity, which involves defining three specific layers:
- Company entities: Clearly defining what your store does and who you serve to establish your brand as an authority in its niche.
- Product entities: Mapping specific features, technical specifications, and use cases to each SKU.
- Problem entities: Identifying the “jobs-to-be-done” or challenges that your products are designed to solve.
When you optimize for a core entity like “ergonomic office chair,” you naturally begin to rank for related concepts like “lumbar support seating” or “adjustable desk chairs.” This happens because Google understands that these terms are conceptually linked to the same entity, even if the exact keywords differ.
Tactics for entity-driven research and optimization
For WooCommerce store owners, entity-driven SEO is about creating a web of relevance around your product catalog. I focus on a few specific tactics to bridge the gap between your inventory and search engine understanding.
Prioritize SERP-based clustering
Avoid the trap of semantic guessing where you assume which keywords belong together. Instead, use actual search engine results to identify entity relationships. If two different keywords return a high percentage of the same URLs in the top 10 results, Google views them as representing the same entity or intent. I recommend using a SERP-based keyword clustering tool to group your terms into logical “content units.” This prevents keyword cannibalization and ensures you are building the specific topical depth search engines demand.
Leverage your first-party search data
Your Google Search Console is the most reliable source of entity data available. Instead of looking at what you already rank for, look for terms that have high impressions but low click-through rates. These often represent unoptimized keywords your site is already associated with, signaling that Google considers you a relevant entity for those topics even if your content isn’t fully meeting the user’s intent yet.
Focus on category-level optimization
A common mistake in ecommerce is pouring all resources into individual product pages while ignoring the category hierarchy. I believe that category pages are the most important assets for capturing broad entity-based traffic. Most stores use vague category names; making them more specific clarifies the entity for search engines and immediately improves discoverability.
Maintain a catalog-aware blog
To dominate AI-driven search, your content must be deeply integrated with your products. Traditional “thought leadership” rarely moves the needle for ecommerce SEO. Instead, we advocate for producing a blog that is synced to your product catalog. If your blog discusses “conical burr grinders,” it should explicitly map the relationship between that attribute entity and the problem entity of “consistent espresso quality.”
Preparing for AI and LLM visibility
The search landscape is shifting toward retrieval rather than just ranking. With consumers increasingly relying on AI for product recommendations, optimizing for LLM retrieval has become a prerequisite for growth. LLMs do not just look for keywords; they retrieve information based on the strength of entity relationships and data structure.
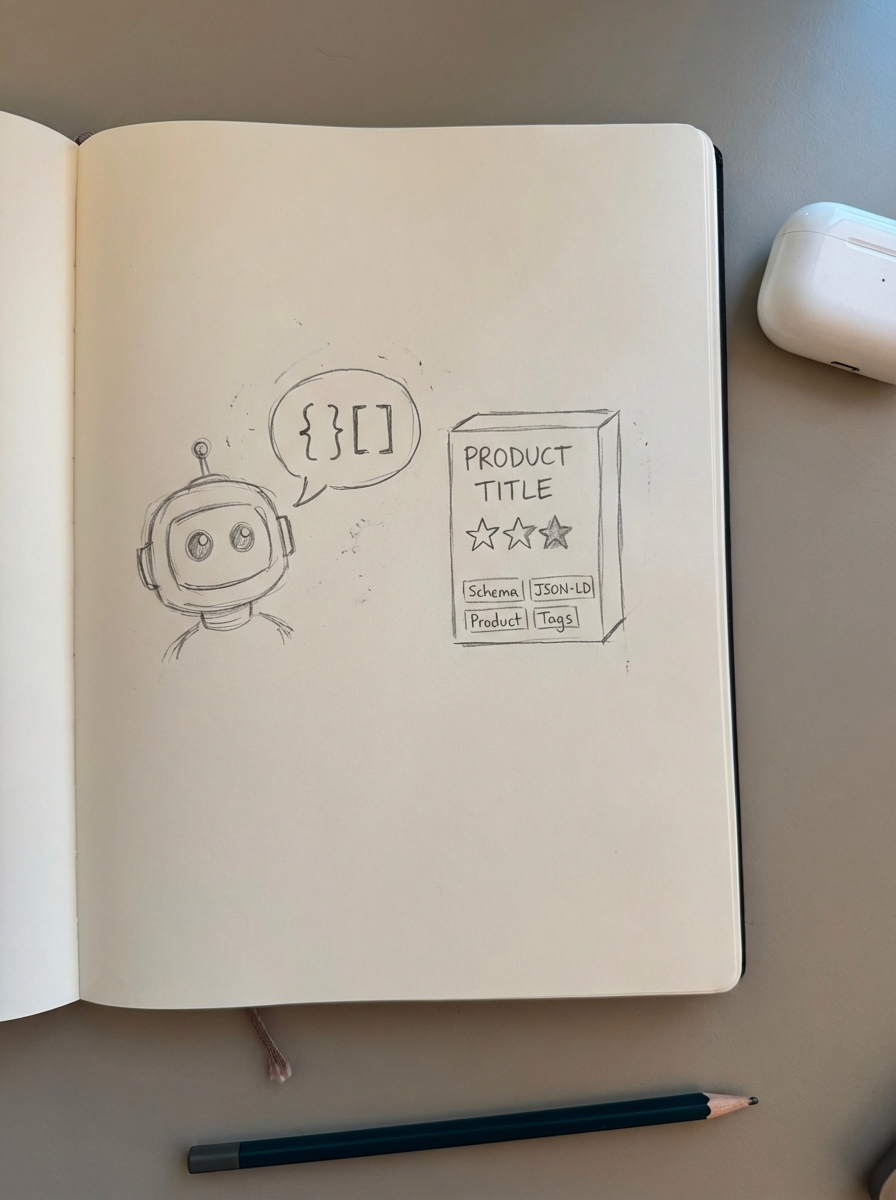
To ensure your store is cited as a source by AI engines, you must focus on technical clarity:
- Explicit Schema Usage: Use JSON-LD to tell search engines exactly what your entities are. Our tactical guide on WooCommerce entity SEO explains how to layer Product, Organization, and Review schema to provide this context.
- Consistent Entity Naming: Ensure you use identical entity names across product titles, headings, and your internal linking structure.
- Descriptive Internal Linking: Move away from generic “click here” anchors. Use entity-rich anchor text that reinforces relationships, such as “how this [conical burr grinder] reduces heat friction.”
TL;DR
Entity-based keyword research shifts the focus from matching search terms to mapping conceptual relationships. By utilizing SERP clustering to group intent, optimizing category names for clarity, and implementing robust product schema, WooCommerce stores can secure higher rankings and better visibility in AI-powered search results. ContentGecko automates this process by keeping your content perfectly synced with your catalog, ensuring your blog remains a high-authority reflection of your product entities.
