Using LLMO for competitive and brand analysis in AI search
Traditional rank tracking is quickly becoming a vanity metric. As large language models (LLMs) and generative search engines begin to mediate the entire buyer’s journey, your visibility is no longer defined by a blue link on page one. If your brand isn’t being cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews, you are effectively invisible to the 58% of consumers who now rely on generative AI for product and service recommendations.
The audit: Measuring your brand’s share of model
The first step in any Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) strategy is auditing your current “Share of Model” (SoM). This allows you to understand how often AI platforms cite your brand compared to your competitors. Unlike traditional SEO, where we obsess over specific SERP positions, LLMO requires us to measure the frequency, context, and sentiment of brand mentions across various generative outputs.
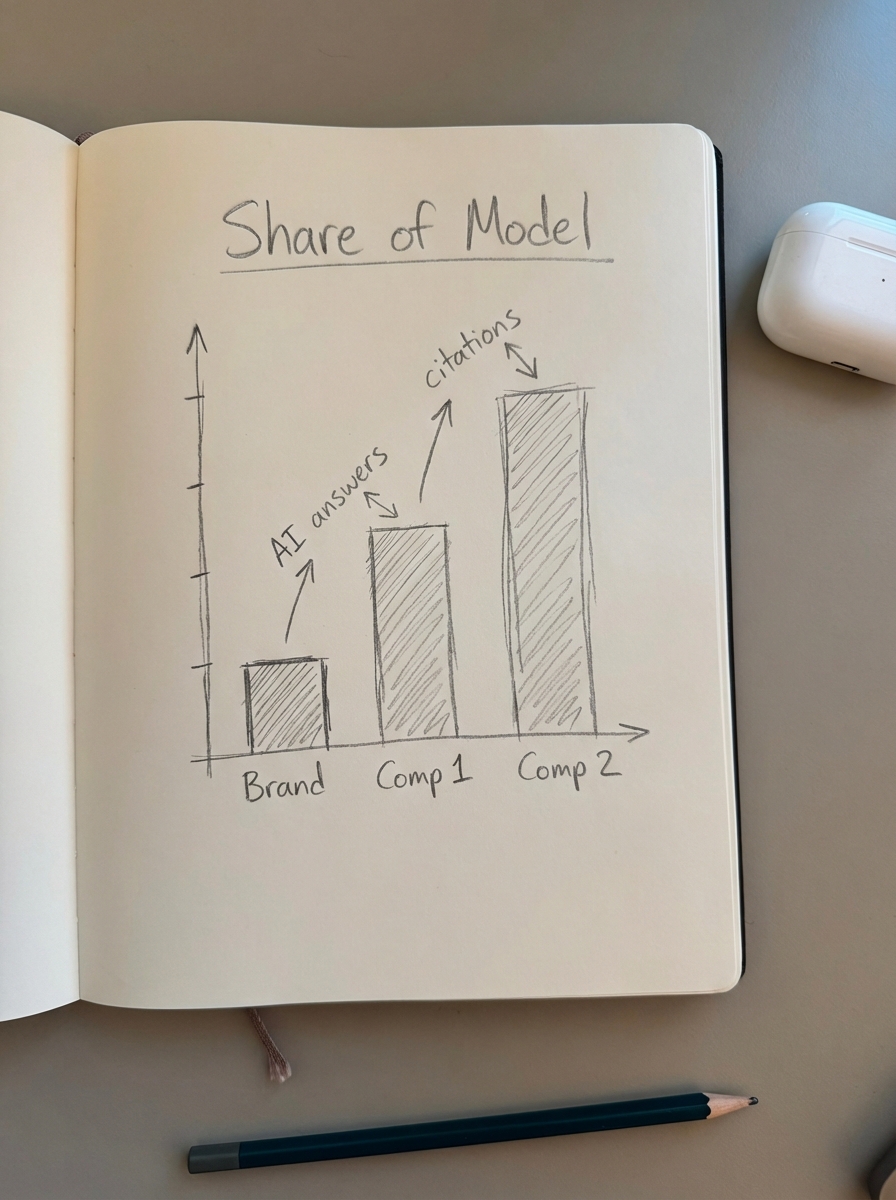
I’ve found that the most effective way to start is by running a baseline audit across the “Big Three”: ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google Gemini. You should query these models with your top-tier commercial keywords, such as “best ergonomic office chairs for back pain,” alongside your brand-specific terms. This identifies if the model associates your store with the core problems you solve.

I often hear marketers argue that because LLM outputs are probabilistic and non-deterministic, these audits are too unreliable to be useful. However, the evidence suggests otherwise. According to recent research into LLMO link building, content reformatted with clear headings and specific citations can increase a brand’s appearance in LLM results by up to 43%. By running multiple iterations of the same prompt, you can establish a statistically significant baseline of your visibility and identify which types of queries you are winning or losing.
To make this data actionable, I recommend using a specialized ecommerce SEO dashboard. This allows you to segment your traffic sources and identify where AI-driven referrals are already landing on your site, moving the audit from theoretical prompts to actual session data.
Benchmarking against competitors in the AI era
Competitive analysis in the age of LLM search shifts the focus from “what keywords do they rank for?” to “how does the AI perceive their entity relationship compared to ours?” AI models build a complex knowledge graph of your industry; you need to know exactly where your brand sits within that graph.
When I conduct competitive benchmarking for WooCommerce stores, I use a framework I call “Entity Gap Analysis.” Instead of just looking at standard competitor keyword gap insights, I prompt an LLM to compare our brand against a rival based on specific user reviews, technical specifications, and value for money.
The AI’s response usually reveals critical strategic gaps. It might highlight perceived weaknesses, such as the AI thinking your shipping is slower than a rival’s based on old forum posts. It can reveal authority gaps, where the AI cites a competitor as an “expert” for a specific product category while ignoring your catalog. It also shows consensus power, indicating if there is a broad consensus across Reddit and niche blogs that favors a competitor for specific use cases.
This is why comparing traditional SEO vs LLMO techniques is so vital for growth leads. Traditional SEO might show you ranking in the second position, but if the AI Overview at the top of the page recommends your competitor as the “best overall” choice, your high ranking is losing its conversion power.
Concrete techniques for influencing AI citations
Once you’ve identified where your brand is lagging in the knowledge graph, you must apply specific LLMO techniques to force the model to reconsider your brand’s authority.
- Entity-based optimization: You must move beyond keywords to entities. This involves ensuring your brand is mentioned in context with other high-authority entities in your niche. I suggest using entity-based keyword research strategies to map out these relationships before writing a single word of content.
- Unlinked brand mentions: Recent data suggests that unlinked brand mentions on high-authority sites now carry significant weight in AI rankings. If influential communities like Reddit or niche forums are discussing your products, the LLM treats that as a strong authority signal, even without a backlink.
- Structured data enrichment: LLMs rely heavily on structured data to parse facts. Implementing robust Product and FAQ schema is non-negotiable for WooCommerce stores that want their pricing, availability, and specs cited accurately.
- Consensus building: LLMs look for “consensus” across the web. If multiple independent sites state that your product is the “most durable” in its class, the LLM will repeat that as a factual recommendation.
I have seen stores significantly boost their citation rate by adding comparison tables and “best for [use case]” headers to their category pages. This makes it incredibly easy for an LLM to scrape and cite your content. If you are struggling to produce this volume of content, a free AI SEO content writer can help generate these citation-ready blocks of text efficiently.
Choosing your LLMO tool stack
Monitoring LLMO performance requires a different set of tools than a standard Ahrefs or Semrush subscription. While those tools are evolving, dedicated trackers are becoming essential for marketing leads who need to prove their AI visibility.
Tools like ZipTie.dev are excellent for tracking visibility specifically within Google’s AI Overviews, while Rankscale.ai is useful for monitoring brand mentions and sentiment across various generative engines. At ContentGecko, our LLMO tool stack essentials emphasize the importance of using systems that understand semantic mapping and structuring data for LLM retrieval.
When selecting a tool, prioritize those that offer “Share of Voice” metrics in AI responses. Knowing your AI citation rate is the modern equivalent of tracking your average position on Google; it is the only way to know if your brand is actually reaching the user before they click a link.
Using insights to prioritize content and SEO actions
The ultimate goal of LLMO competitive analysis is to inform your content roadmap. If the AI is consistently citing a competitor for “eco-friendly materials” but ignoring your brand, that is a clear signal to double down on content that establishes your authority in that specific sub-topic.
I recommend a prioritization process focused on the “citation gap.” First, identify which commercial queries you are losing in AI Overviews. Next, use SERP-based keyword clustering to see if the AI groups those queries into a single intent that you haven’t covered comprehensively. Finally, deploy fact-heavy content that replaces generic marketing copy with specific data points, expert quotes, and comparison tables.
We have observed that WooCommerce stores which prioritize optimizing category pages with educational content – rather than just product grids – see much higher referral rates from models like Perplexity.
Some critics argue that AI content is prone to hallucinations and shouldn’t be trusted for analysis. In my experience, AI only hallucinates in competitive analysis when you haven’t provided enough context or when your site’s metadata is disorganized. When you provide an LLM with structured product data and clear entity relationships, its ability to compare you against a competitor is surprisingly accurate and provides insights that traditional SEO tools simply cannot see.
TL;DR
- Measure your “Share of Model” across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini to establish a visibility baseline.
- Use AI prompts to find perception gaps between your brand and your competitors’ authority.
- Focus on structured data, unlinked mentions, and entity-based SEO to influence how AI models cite your products.
- Shift your tracking from traditional positions to new metrics like AI citation rates and semantic accuracy.
- Use LLMO insights to fill content gaps and establish consensus-based authority for your most important product categories.
